H-D-Leu-OH
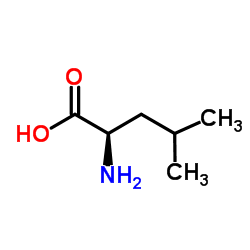
H-D-Leu-OH structure
|
Common Name | H-D-Leu-OH | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 328-38-1 | Molecular Weight | 131.173 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 225.8±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H13NO2 | Melting Point | > 300ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 90.3±22.6 °C | |
Use of H-D-Leu-OHD-Leucine is a more potent anti-seizure agent than L-leucine. D-leucine potently terminates seizures even after the onset of seizure activity. D-leucine, but not L-leucine, reduces long-term potentiation but had no effect on basal synaptic transmission in vitro[1]. |
| Name | D-leucine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | D-Leucine is a more potent anti-seizure agent than L-leucine. D-leucine potently terminates seizures even after the onset of seizure activity. D-leucine, but not L-leucine, reduces long-term potentiation but had no effect on basal synaptic transmission in vitro[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vitro | In a screen of candidate neuronal receptors, D-leucine failed to compete for binding by cognate ligands, potentially suggesting a novel target. Even at low doses, D-leucine suppressed ongoing seizures at least as effectively as diazepam but without sedative effects. These studies raise the possibility that D-leucine may represent a new class of anti-seizure agents, and that D-leucine may have a previously unknown function in eukaryotes[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 225.8±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | > 300ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C6H13NO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 131.173 |
| Flash Point | 90.3±22.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 131.094635 |
| PSA | 63.32000 |
| LogP | 0.73 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.463 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | 22-24/25-36-26 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | OH2840000 |
| HS Code | 2922499990 |
| Precursor 6 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2922499990 |
|---|---|
| Summary | HS:2922499990 other amino-acids, other than those containing more than one kind of oxygen function, and their esters; salts thereof VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:AB(certificate of inspection for goods inward,certificate of inspection for goods outward) MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Defining transcribed regions using RNA-seq.
Nat. Protoc. 5 , 255-66, (2010) Next-generation sequencing technologies are revolutionizing genomics research. It is now possible to generate gigabase pairs of DNA sequence within a week without time-consuming cloning or massive inf... |
|
|
Dietary leucine--an environmental modifier of insulin resistance acting on multiple levels of metabolism.
PLoS ONE 6(6) , e21187, (2011) Environmental factors, such as the macronutrient composition of the diet, can have a profound impact on risk of diabetes and metabolic syndrome. In the present study we demonstrate how a single, simpl... |
|
|
Potent anti-seizure effects of D-leucine.
Neurobiol. Dis. 82 , 46-53, (2015) There are no effective treatments for millions of patients with intractable epilepsy. High-fat ketogenic diets may provide significant clinical benefit but are challenging to implement. Low carbohydra... |
| leucine |
| D-Leucine |
| MFCD00063088 |
| (R)-2-Amino-4-methylpentanoic acid |
| (2R)-2-amino-4-methylpentanoic acid |
| ent-1 |
| H-Leu-OH |
| D-Homo-valine |
| D-2-Amino-4-methylvaleric acid |
| H-D-Leu-OH |
| (R)-2-Amino-4-methyl-pentanoic acid |
| Leucine, D- |
| EINECS 206-327-7 |
| D-2-Amino-4-methylpentanoicacid |
 CAS#:24292-07-7
CAS#:24292-07-7 CAS#:161633-97-2
CAS#:161633-97-2 CAS#:328-39-2
CAS#:328-39-2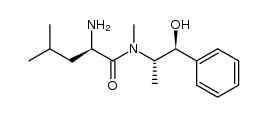 CAS#:170642-24-7
CAS#:170642-24-7 CAS#:89384-51-0
CAS#:89384-51-0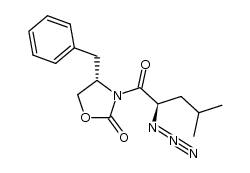 CAS#:113543-42-3
CAS#:113543-42-3 CAS#:19892-92-3
CAS#:19892-92-3 CAS#:816-66-0
CAS#:816-66-0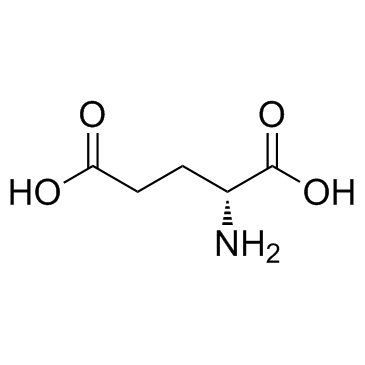 CAS#:6893-26-1
CAS#:6893-26-1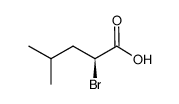 CAS#:28659-87-2
CAS#:28659-87-2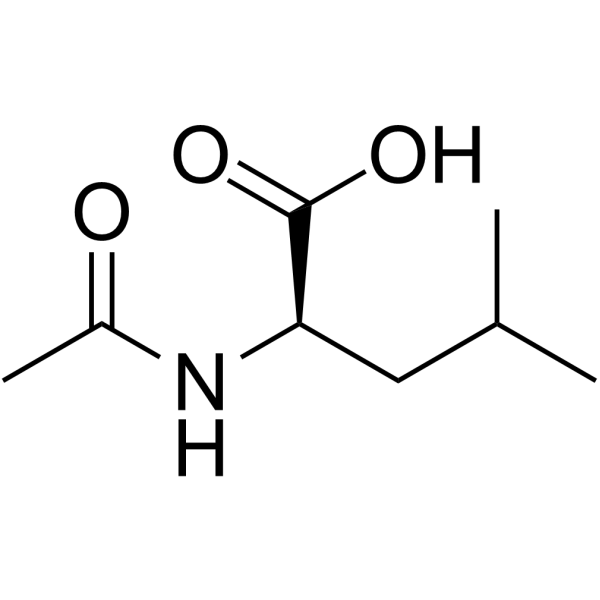 CAS#:19764-30-8
CAS#:19764-30-8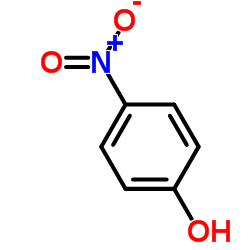 CAS#:100-02-7
CAS#:100-02-7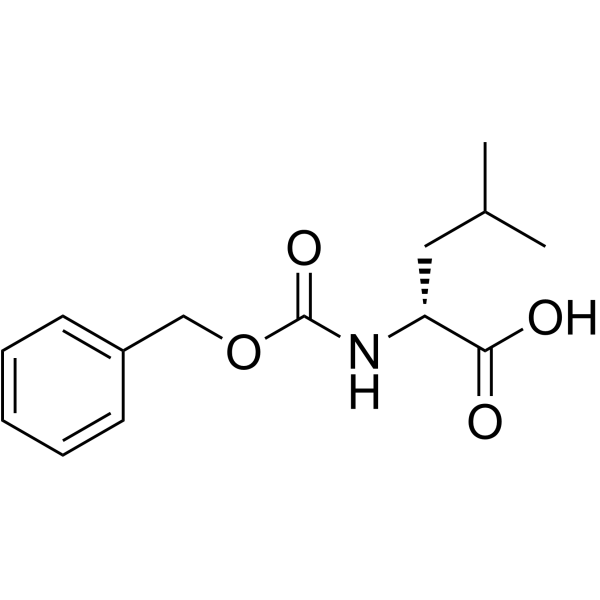 CAS#:28862-79-5
CAS#:28862-79-5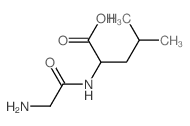 CAS#:688-13-1
CAS#:688-13-1 CAS#:5845-53-4
CAS#:5845-53-4
