Mirin
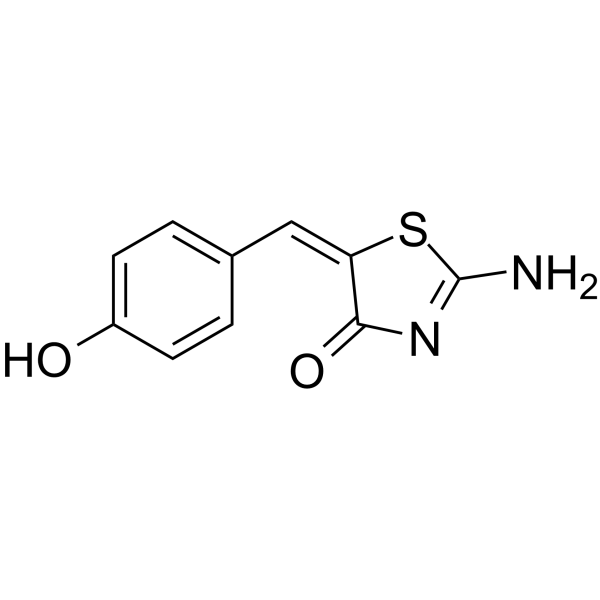
Mirin structure
|
Common Name | Mirin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 299953-00-7 | Molecular Weight | 220.248 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 441.6±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H8N2O2S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 220.8±31.5 °C | |
Use of MirinMirin is a potent Mre11-Rad50-Nbs1 (MRN) complex inhibitor. Mirin prevents MRN-dependent activation of ATM (IC50=12 μM) without affecting ATM protein kinase activity, and it inhibits Mre11-associated exonuclease activity. Mirin abolishes the G2/M checkpoint and homology-dependent repair in mammalian cells. Mirin prevents ATM activation in response to DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) and blocks homology-directed repair (HDR) in mammalian cells[1]. |
| Name | 2-amino-5-[(4-hydroxyphenyl)methylidene]-1,3-thiazol-4-one |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Mirin is a potent Mre11-Rad50-Nbs1 (MRN) complex inhibitor. Mirin prevents MRN-dependent activation of ATM (IC50=12 μM) without affecting ATM protein kinase activity, and it inhibits Mre11-associated exonuclease activity. Mirin abolishes the G2/M checkpoint and homology-dependent repair in mammalian cells. Mirin prevents ATM activation in response to DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) and blocks homology-directed repair (HDR) in mammalian cells[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Mirin inhibits H2AX phosphorylation with an IC50 of 66 μM. Mirin also inhibits the ATM-dependent phosphorylation of the downstream targets Nbs1 and Chk2 and the MRN-dependent autophosphorylation of ATM at Ser1981 in response to DSBs. Mirin induces a substantial G2 arrest at concentrations of 50 μM and 100 μM. Mirin (10-100 μM) inhibits homology-dependent DNA repair in TOSA4 cells[1]. BRCA2-deficient cells also showed hypersensitivity to the Mre11 inhibitor Mirin[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 441.6±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C10H8N2O2S |
| Molecular Weight | 220.248 |
| Flash Point | 220.8±31.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 220.030655 |
| PSA | 98.48000 |
| LogP | 1.36 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.718 |
| InChIKey | YBHQCJILTOVLHD-YVMONPNESA-N |
| SMILES | NC1=NC(=O)C(=Cc2ccc(O)cc2)S1 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|---|---|
| HS Code | 2934999090 |
| Precursor 2 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
| HS Code | 2934999090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2934999090. other heterocyclic compounds. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Productive replication of human papillomavirus 31 requires DNA repair factor Nbs1.
J. Virol. 88(15) , 8528-44, (2014) Activation of the ATM (ataxia telangiectasia-mutated kinase)-dependent DNA damage response (DDR) is necessary for productive replication of human papillomavirus 31 (HPV31). We previously found that DN... |
|
|
DNA double-strand break repair pathway choice is directed by distinct MRE11 nuclease activities.
Mol. Cell. 53(1) , 7-18, (2014) MRE11 within the MRE11-RAD50-NBS1 (MRN) complex acts in DNA double-strand break repair (DSBR), detection, and signaling; yet, how its endo- and exonuclease activities regulate DSBR by nonhomologous en... |
|
|
A central role of TRAX in the ATM-mediated DNA repair.
Oncogene 35 , 1657-70, (2016) DNA repair is critical for the maintenance of genome stability. Upon genotoxic stress, dysregulated DNA repair may induce apoptosis. Translin-associated factor X (TRAX), which was initially identified... |
| 5-(4-Hydroxy-benzylidene)-2-imino-thiazolidin-4-one |
| 4(5H)-Thiazolone, 2-amino-5-[(4-hydroxyphenyl)methylene]-, (5Z)- |
| Mirin |
| (5Z)-2-Amino-5-(4-hydroxybenzylidene)-1,3-thiazol-4(5H)-one |
| 4-Thiazolidinone, 5-(p-hydroxybenzylidene)-2-imino- |
| MRN-ATM Pathway Inhibitor,Mirin |
| Lu AA 47070 |