25-Hydroxycholesterol
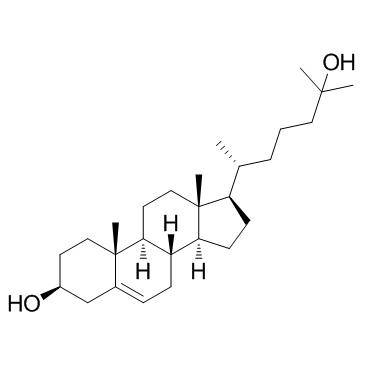
25-Hydroxycholesterol structure
|
Common Name | 25-Hydroxycholesterol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 2140-46-7 | Molecular Weight | 402.653 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 513.1±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C27H46O2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 213.5±17.2 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of 25-Hydroxycholesterol25-Hydroxycholesterol is a metabolite of cholesterol that is produced and secreted by macrophages in response to Toll-like receptor (TLR) activation. 25-hydroxycholesterol is a potent (EC50≈65 nM) and selective suppressor of IgA production by B cells. |
| Name | 25-hydroxycholesterol |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | 25-Hydroxycholesterol is a metabolite of cholesterol that is produced and secreted by macrophages in response to Toll-like receptor (TLR) activation. 25-hydroxycholesterol is a potent (EC50≈65 nM) and selective suppressor of IgA production by B cells. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vitro | The synthesis of 25-hydroxycholesterol is catalyzed by the enzyme cholesterol 25-hydroxylase, which uses cholesterol and molecular oxygen as substrates and NADPH as a cofactor. 25-hydroxycholesterol is a potent bioactive lipid in the innate and adaptive immune systems[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 513.1±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C27H46O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 402.653 |
| Flash Point | 213.5±17.2 °C |
| Exact Mass | 402.349792 |
| PSA | 40.46000 |
| LogP | 7.66 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.538 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H312-H315-H319-H332-H335-H373 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P280-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Hazard Codes | Xn: Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | 20/21/22-36/37/38-48 |
| Safety Phrases | 26-36-45 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|
Oxysterols synergize with statins by inhibiting SREBP-2 in ovarian cancer cells.
Gynecol. Oncol. 135(2) , 333-41, (2014) Determine mechanisms responsible for enhanced statin efficacy in a novel statin combination we name STOX (STatin-OXysterol).Ovarian cancer cell lines were treated with combinations of statins and oxys... |
|
|
The effects of Zanthoxylum bungeanum extract on lipid metabolism induced by sterols.
J. Pharmacol. Sci. 127(3) , 251-9, (2015) Variant pharmacological activities of Zanthoxylum bungeanum were determined before. The aim of this study was to assess whether Z. bungeanum could regulate lipid metabolism. The cholesterol overloadin... |
|
|
Specific cellular incorporation of a pyrene-labelled cholesterol: lipoprotein-mediated delivery toward ordered intracellular membranes.
PLoS ONE 10(4) , e0121563, (2015) In the aim of testing tools for tracing cell trafficking of exogenous cholesterol, two fluorescent derivatives of cholesterol, 22-nitrobenzoxadiazole-cholesterol (NBD-Chol) and 21-methylpyrenyl-choles... |
| 25-Hydroxy Cholesterol |
| (3β,9β,14β)-Cholest-5-ene-3,25-diol |
| Cholest-5-ene-3,25-diol, (3β,9β,14β)- |
| (3S,8S,9S,10R,13R,14S,17R)-17-[(2R)-6-hydroxy-6-methylheptan-2-yl]-10,13-dimethyl-2,3,4,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-dodecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-ol |

