Sodium taurodeoxycholate hydrate
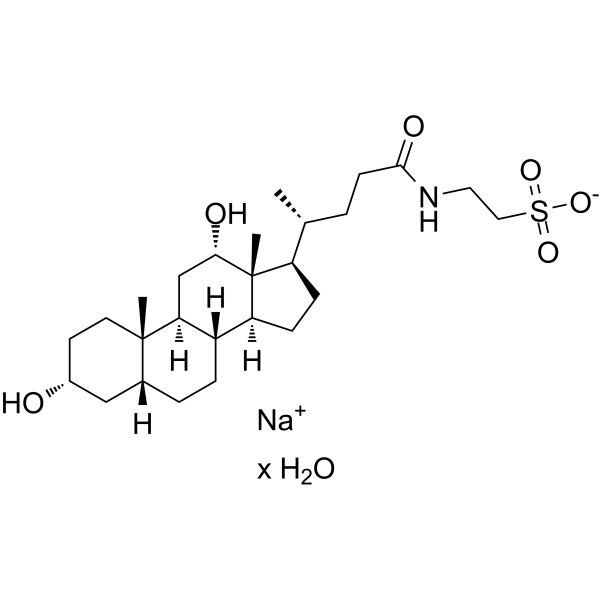
Sodium taurodeoxycholate hydrate structure
|
Common Name | Sodium taurodeoxycholate hydrate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 207737-97-1 | Molecular Weight | 521.69 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C26H44NNaO6S | Melting Point | 168ºC (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Name | Sodium taurodeoxycholate hydrate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description |
|---|
| Melting Point | 168ºC (dec.)(lit.) |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C26H44NNaO6S |
| Molecular Weight | 521.69 |
| Exact Mass | 539.289246 |
| PSA | 144.37000 |
| LogP | 4.46210 |
| InChIKey | OLPIZAYYAVQETM-GGPRKOIFSA-M |
| SMILES | CC(CCC(=O)NCCS(=O)(=O)[O-])C1CCC2C3CCC4CC(O)CCC4(C)C3CC(O)C12C.O.[Na+] |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3.0 |
|
Shiga toxin glycosphingolipid receptors of Vero-B4 kidney epithelial cells and their membrane microdomain lipid environment.
J. Lipid Res. 56 , 2322-36, (2015) Shiga toxins (Stxs) are produced by enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC), which cause human infections with an often fatal outcome. Vero cell lines, derived from African green monkey kidney, repr... |
|
|
Bile acids repress hypoxia-inducible factor 1 signaling and modulate the airway immune response.
Infect. Immun. 82(9) , 3531-41, (2014) Gastroesophageal reflux (GER) frequently occurs in patients with respiratory disease and is particularly prevalent in patients with cystic fibrosis. GER is a condition in which the duodenogastric cont... |
|
|
Regulation of host weight gain and lipid metabolism by bacterial bile acid modification in the gut.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 111(20) , 7421-6, (2014) Alterations in the gastrointestinal microbiota have been implicated in obesity in mice and humans, but the key microbial functions influencing host energy metabolism and adiposity remain to be determi... |
| Ethanesulfonic acid, 2-[[(3α,5β,12α)-3,12-dihydroxy-24-oxocholan-24-yl]amino]-, sodium salt, hydrate (1:1:1) |
| taurodeoxycholic acid sodium sigmaultra |
| Sodium 2-{[(3α,5β,12α)-3,12-dihydroxy-24-oxocholan-24-yl]amino}ethanesulfonate hydrate (1:1:1) |
| MFCD00149238 |
