Saccharin sodium hydrate
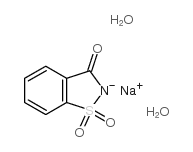
Saccharin sodium hydrate structure
|
Common Name | Saccharin sodium hydrate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 82385-42-0 | Molecular Weight | 241.19700 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 438.9ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C7H8NNaO5S | Melting Point | >300°C | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 219.3ºC | |
Use of Saccharin sodium hydrateSaccharin sodium hydrate is an orally active, non-caloric artificial sweeteners (NAS). Saccharin sodium hydrate has bacteriostatic and microbiome-modulating properties[1]. |
| Name | Saccharin, sodium salt hydrate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Saccharin sodium hydrate is an orally active, non-caloric artificial sweeteners (NAS). Saccharin sodium hydrate has bacteriostatic and microbiome-modulating properties[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | In vitro, saccharin sodium hydrate (0.5, 2.5, 5 mM) inhibits bacterial growth in a species-dependent manner[1]. |
| In Vivo | In vivo, saccharin sodium hydrate (oral; 5 mg/kg; twice a day) intake reduces fecal bacterial load and alters microbiome composition, while the intestinal barrier is not obviously affected in male C57BL/6JRj wild type (wt) mice[1]. |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 438.9ºC at 760 mmHg |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | >300°C |
| Molecular Formula | C7H8NNaO5S |
| Molecular Weight | 241.19700 |
| Flash Point | 219.3ºC |
| Exact Mass | 241.00200 |
| PSA | 78.05000 |
| LogP | 1.18550 |
| Water Solubility | H2O: 1 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless |
|
Fructose- and glucose-conditioned preferences in FVB mice: strain differences in post-oral sugar appetition.
Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 307(12) , R1448-57, (2014) Recent studies indicate that, unlike glucose, fructose has little or no post-oral preference conditioning actions in C57BL/6J (B6) mice. The present study determined whether this is also the case for ... |
|
|
Common-ion effects on the deliquescence lowering of crystalline ingredient blends.
Food Chem. 195 , 2-10, (2015) Deliquescence points (RH0, RH0mix) of ionic crystalline food ingredients and blends thereof were determined using water activity and moisture sorption techniques. Measured RH0mix values of ingredient ... |
|
|
Role of olfaction in the conditioned sucrose preference of sweet-ageusic T1R3 knockout mice.
Chem. Senses 34 , 685-94, (2009) Prior work has shown that sweet taste-deficient T1R3 knockout (KO) mice developed significant sucrose preferences when given long-term sugar versus water tests. The current study investigated the role... |
| MFCD00151213 |
| EINECS 204-886-1 |
| saccharin sodium salt dihydrate |

