4-Chlorophenylacetic acid
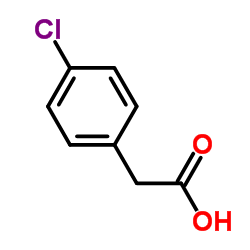
4-Chlorophenylacetic acid structure
|
Common Name | 4-Chlorophenylacetic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1878-66-6 | Molecular Weight | 170.593 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 294.1±15.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H7ClO2 | Melting Point | 102-105 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 131.7±20.4 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of 4-Chlorophenylacetic acid4-Chlorophenylacetic acid is a compound belongs to a family of small aromatic fatty acids with anticancer properties. 4-Chlorophenylacetic acid can provide carbon and energy for Pseudomonas sp[1][2]. |
| Name | 4-chlorophenylacetic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | 4-Chlorophenylacetic acid is a compound belongs to a family of small aromatic fatty acids with anticancer properties. 4-Chlorophenylacetic acid can provide carbon and energy for Pseudomonas sp[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 294.1±15.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 102-105 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C8H7ClO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 170.593 |
| Flash Point | 131.7±20.4 °C |
| Exact Mass | 170.013458 |
| PSA | 37.30000 |
| LogP | 2.10 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.570 |
| InChIKey | CDPKJZJVTHSESZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | O=C(O)Cc1ccc(Cl)cc1 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H312 + H332 |
| Precautionary Statements | P280 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn: Harmful;Xi: Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R20/21 |
| Safety Phrases | S36/37-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | AG0590000 |
| HS Code | 2916340090 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2916399090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2916399090 other aromatic monocarboxylic acids, their anhydrides, halides, peroxides, peroxyacids and their derivatives VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Novel Chryseobacterium sp. PYR2 degrades various organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) and achieves enhancing removal and complete degradation of DDT in highly contaminated soil.
J. Environ. Manage. 161 , 350-7, (2015) Long term residues of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in soils are of great concerning because they seriously threaten food security and human health. This article focuses on isolation of OCP-degradi... |
|
|
Degradation of 4-chlorophenylacetic acid by a Pseudomonas species.
J. Bacteriol. 146(1) , 64-8, (1981) Pseudomonas sp. strain CBS3 was able to utilize 4-chlorophenylacetic acid as the sole source of carbon and energy. When this strain was grown with 4-chlorophenylacetic acid, homoprotocatechuic acid wa... |
|
|
Inhibition of estrogen-induced mammary tumor formation in MMTV-aromatase transgenic mice by 4-chlorophenylacetate.
Cancer Lett. 251(2) , 302-10, (2007) Treatment of estrogen-sensitive breast cancer with selective estrogen selective modulators (SERMs) and, more recently, aromatase inhibitors has met with wide success. However, antagonism of estrogen r... |
| EINECS 217-521-6 |
| Acetic acid, 4-chlorophenyl- |
| (4-Chlorophenyl)acetic acid |
| 4-Chlorobenzeneacetic acid |
| 4-Chlorophenylacetic acid |
| 2-(4-chloro-phenyl)-acetic acid |
| p-chlorophenylacetate |
| Acetic acid,(p-chlorophenyl) |
| 4-Cl-phenylacetic acid |
| p-chlorophenyl acetic acid |
| Benzeneacetic acid,4-chloro |
| Benzeneacetic acid, 4-chloro- |
| 2-(4-chlorophenyl)acetic acid |
| P-CHLOROPHENYLACETIC ACID |
| 2-(p-Chlorophenyl)acetic acid |
| 4-ClPhCH2CO2H |
| Acetic acid, (p-chlorophenyl)- |
| MFCD00004344 |
 CAS#:201230-82-2
CAS#:201230-82-2 CAS#:104-83-6
CAS#:104-83-6 CAS#:14062-24-9
CAS#:14062-24-9 CAS#:140-53-4
CAS#:140-53-4 CAS#:622-95-7
CAS#:622-95-7 CAS#:1875-88-3
CAS#:1875-88-3 CAS#:77295-59-1
CAS#:77295-59-1 CAS#:52449-43-1
CAS#:52449-43-1 CAS#:62037-06-3
CAS#:62037-06-3 CAS#:373-91-1
CAS#:373-91-1![Benzeneacetic acid,4-chloro-a-[(2-nitrophenyl)methylene]- structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/299/10465-92-6.png) CAS#:10465-92-6
CAS#:10465-92-6 CAS#:101492-44-8
CAS#:101492-44-8 CAS#:5468-66-6
CAS#:5468-66-6 CAS#:32327-71-2
CAS#:32327-71-2 CAS#:1195-44-4
CAS#:1195-44-4 CAS#:3395-81-1
CAS#:3395-81-1 CAS#:104-88-1
CAS#:104-88-1 CAS#:873-76-7
CAS#:873-76-7 CAS#:37777-68-7
CAS#:37777-68-7
