4-Hydroxyphenylacetonitrile

4-Hydroxyphenylacetonitrile structure
|
Common Name | 4-Hydroxyphenylacetonitrile | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 14191-95-8 | Molecular Weight | 133.15 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 331.8±44.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | HOC6H4CH2CN | Melting Point | 71°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 154.5±28.4 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of 4-Hydroxyphenylacetonitrile4-Hydroxybenzyl cyanide is an endogenous metabolite. |
| Name | (4-hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | 4-Hydroxybenzyl cyanide is an endogenous metabolite. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 331.8±44.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 71°C |
| Molecular Formula | HOC6H4CH2CN |
| Molecular Weight | 133.15 |
| Flash Point | 154.5±28.4 °C |
| PSA | 44.02000 |
| LogP | -2.42 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.579 |
| Water Solubility | slightly soluble |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H312-H332 |
| Precautionary Statements | P280 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful |
| Risk Phrases | R20/21/22;R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S36/37-S36/37/39-S26 |
| RIDADR | 3439 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | AM0530000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1 |
| HS Code | 2926909090 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2926909090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | HS:2926909090 other nitrile-function compounds VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Formation of trichloronitromethane and dichloroacetonitrile in natural waters: precursor characterization, kinetics and interpretation.
J. Hazard. Mater. 283 , 218-26, (2014) During the chloramination of natural waters, both chloramines and dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) can serve as nitrogen sources for the formation of trichloronitromethane (TCNM) and dichloroacetonitr... |
|
|
Supercritical fluid chromatography as a method of analysis for the determination of 4-hydroxybenzylglucosinolate degradation products.
J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 43(1-3) , 157-74, (2000) In the present study analytical and preparative supercritical fluid chromatography (SFC) were used for investigation of myrosinase catalysed degradation of 4-hydroxybenzylglucosinolate (sinalbin). Sin... |
|
|
Tyrosinase kinetics: failure of the auto-activation mechanism of monohydric phenol oxidation by rapid formation of a quinomethane intermediate.
Biochem. J. 333 ( Pt 3) , 685-91, (1998) When 3,4-dihydroxybenzylcyanide (DBC) is oxidized by mushroom tyrosinase, the first visible product, identified as the corresponding quinomethane, exhibits an absorption maximum at 480 nm. Pulse-radio... |
| 4-Hydroxyphenylacetonitrile |
| Pentanoic acid, 5-[(aminoiminomethyl)amino]-2-oxo- |
| MFCD00002383 |
| 5-guanidino-2-oxopentanoic acid zwitterion |
| 4-Hydroxybenzyl Cyanide |
| 5-guanidino-2-oxopentanoic acid |
| 2-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile |
| EINECS 238-046-0 |
| 5-Carbamimidamido-2-oxopentanoic acid |
 CAS#:104-47-2
CAS#:104-47-2 CAS#:107-31-3
CAS#:107-31-3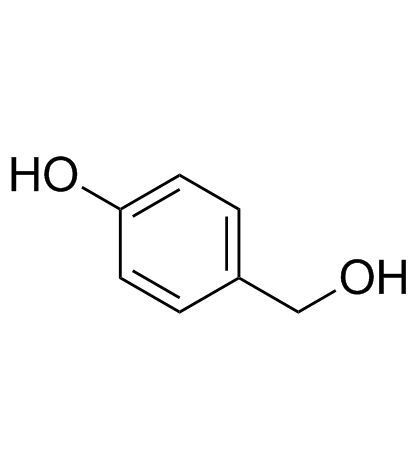 CAS#:623-05-2
CAS#:623-05-2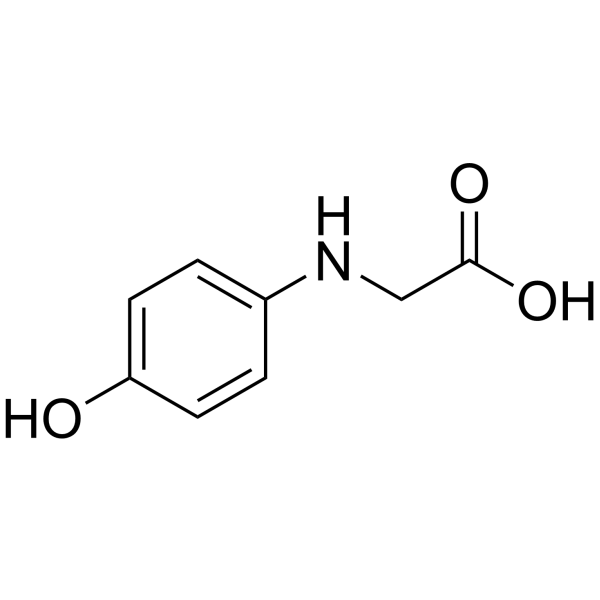 CAS#:122-87-2
CAS#:122-87-2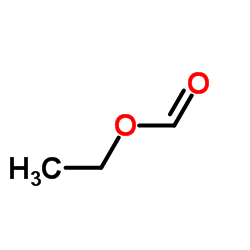 CAS#:109-94-4
CAS#:109-94-4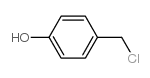 CAS#:35421-08-0
CAS#:35421-08-0 CAS#:838-96-0
CAS#:838-96-0 CAS#:110-74-7
CAS#:110-74-7 CAS#:4985-46-0
CAS#:4985-46-0 CAS#:60-18-4
CAS#:60-18-4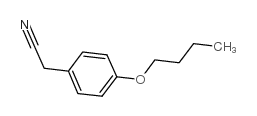 CAS#:38746-93-9
CAS#:38746-93-9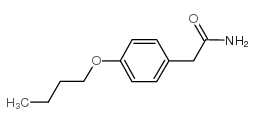 CAS#:3413-59-0
CAS#:3413-59-0 CAS#:4919-33-9
CAS#:4919-33-9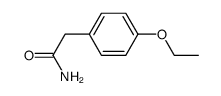 CAS#:40784-91-6
CAS#:40784-91-6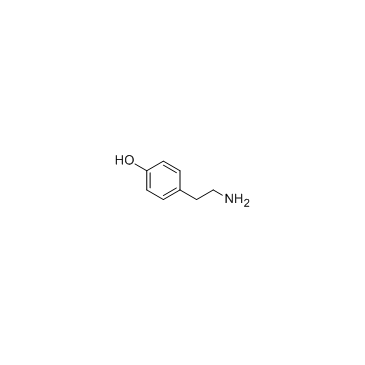 CAS#:51-67-2
CAS#:51-67-2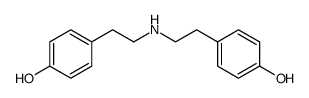 CAS#:702695-10-1
CAS#:702695-10-1 CAS#:106-44-5
CAS#:106-44-5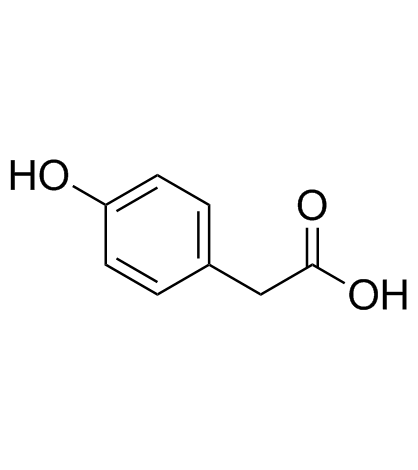 CAS#:156-38-7
CAS#:156-38-7 CAS#:446-72-0
CAS#:446-72-0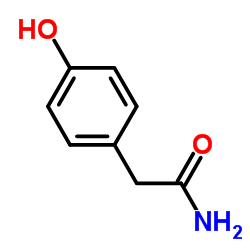 CAS#:17194-82-0
CAS#:17194-82-0
