Arvanil
Arvanil structure
|
Common Name | Arvanil | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 128007-31-8 | Molecular Weight | 439.63 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 619.4±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
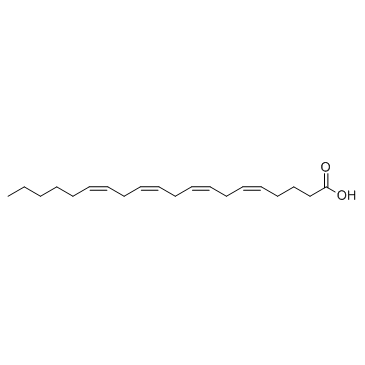
| Molecular Formula | C28H41NO3 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 328.4±31.5 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS02, GHS07 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of ArvanilArvanil is a ligand for vanilloid receptor 1 (VR1) and cannabinoid 1 (CB1). Arvanil can inhibit spasticity, as a potent neuroprotectant[1]. |
| Name | Arvanil,N-[(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z-eicosatetraenamide |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Arvanil is a ligand for vanilloid receptor 1 (VR1) and cannabinoid 1 (CB1). Arvanil can inhibit spasticity, as a potent neuroprotectant[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
VR1, CB1[1] |
| References |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 619.4±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C28H41NO3 |
| Molecular Weight | 439.63 |
| Flash Point | 328.4±31.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 439.308655 |
| PSA | 58.56000 |
| LogP | 7.00 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.533 |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS02, GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H225-H319 |
| Precautionary Statements | P210-P305 + P351 + P338-P370 + P378-P403 + P235 |
| RIDADR | UN1170 - class 3 - PG 2 - Ethanol |
|
~96% 
Arvanil CAS#:128007-31-8 |
| Literature: Appendino, Giovanni; Minassi, Alberto; Morello, Aniello Schiano; De Petrocellis, Luciano; Di Marzo, Vincenzo Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2002 , vol. 45, # 17 p. 3739 - 3745 |
|
~% 
Arvanil CAS#:128007-31-8 |
| Literature: Janusz, John M.; Buckwalter, Brian L.; Young, Patricia A.; LaHann, Thomas R.; Farmer, Ralph W.; et al. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 1993 , vol. 36, # 18 p. 2595 - 2604 |
|
~33% 
Arvanil CAS#:128007-31-8 |
| Literature: Janusz, John M.; Buckwalter, Brian L.; Young, Patricia A.; LaHann, Thomas R.; Farmer, Ralph W.; et al. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 1993 , vol. 36, # 18 p. 2595 - 2604 |
|
Genetic background can result in a marked or minimal effect of gene knockout (GPR55 and CB2 receptor) in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis models of multiple sclerosis.
PLoS ONE 8 , e76907, (2013) Endocannabinoids and some phytocannabinoids bind to CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors, transient receptor potential vanilloid one (TRPV1) receptor and the orphan G protein receptor fifty-five (GPR55).... |
| (5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)-N-(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxybenzyl)-5,8,11,14-icosatetraenamide |
| N-vanillyl-5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z-eicosatetraenamide |
| 5,8,11,14-Eicosatetraenamide, N-[(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-, (5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)- |
| ARVANIL |
| Picrotoxin |
| (5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)-N-(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxybenzyl)icosa-5,8,11,14-tetraenamide |
| N-arachidonoylvanillamine |
| N-VANILLYLARACHIDONAMIDE |
| MFCD01752675 |