5(6)-Carboxyfluorescein Diacetate
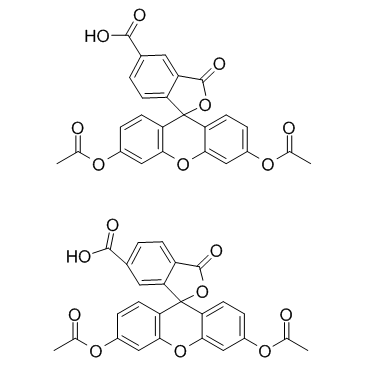
5(6)-Carboxyfluorescein Diacetate structure
|
Common Name | 5(6)-Carboxyfluorescein Diacetate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 124387-19-5 | Molecular Weight | 460.39 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C25H16O9 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of 5(6)-Carboxyfluorescein Diacetate5(6)-CFDA is a cell-permeant esterase substrate that can serve as a viability probe that measures both enzymatic activity, which is require to activate its fluorescence, and cell-membrane integrity, which is required for intracellular retention of their fluorescent product. |
| Name | 5(6)-Carboxyfluorescein diacetate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | 5(6)-CFDA is a cell-permeant esterase substrate that can serve as a viability probe that measures both enzymatic activity, which is require to activate its fluorescence, and cell-membrane integrity, which is required for intracellular retention of their fluorescent product. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C25H16O9 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 460.39 |
| PSA | 250.86000 |
| LogP | 7.60680 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|
Contractile activity of human follicular dendritic cells.
Immunol. Cell Biol. 92(10) , 851-9, (2014) Follicular dendritic cells (FDCs) present antigens to B cells in the lymphoid follicle and inhibit B-cell apoptosis. In previous work, we obtained human FDC lines that allowed us to study the antigen ... |
|
|
Chloroplasts extend stromules independently and in response to internal redox signals.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 112 , 10044-9, (2015) A fundamental mystery of plant cell biology is the occurrence of "stromules," stroma-filled tubular extensions from plastids (such as chloroplasts) that are universally observed in plants but whose fu... |
|
|
Effects of vitamin D receptor knockout on cornea epithelium gap junctions.
Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 55(5) , 2975-82, (2014) Gap junctions are present in all corneal cell types and have been shown to have a critical role in cell phenotype determination. Vitamin D has been shown to influence cell differentiation, and recent ... |
| 3',6'-diacetyloxy-1-oxospiro[2-benzofuran-3,9'-xanthene]-4-carboxylic acid,3',6'-diacetyloxy-1-oxospiro[2-benzofuran-3,9'-xanthene]-5-carboxylic acid |
| 5(6)-Carboxy-di-O-acetylfluorescein |
| 3',6'-Diacetoxy-3-oxo-3H-spiro[2-benzofuran-1,9'-xanthene]-6-carboxylic acid - 3',6'-diacetoxy-3-oxo-3H-spiro[2-benzofuran-1,9'-xanthene]-7-carboxylic acid (1:1) |
| Spiro[isobenzofuran-1(3H),9'-[9H]xanthene]-6-carboxylic acid, 3',6'-bis(acetyloxy)-3-oxo-, compd. with 3',6'-bis(acetyloxy)-3-oxospiro[isobenzofuran-1(3H),9'-[9H]xanthene]-7-carboxylic acid (1:1) |
| 5(6)-CFDA |

