salvianolic acid B
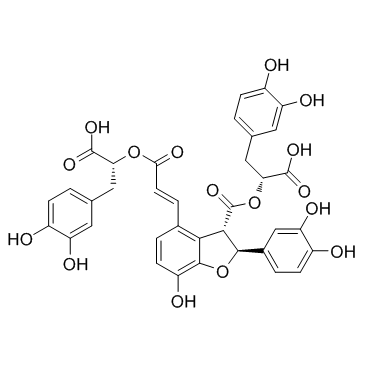
salvianolic acid B structure
|
Common Name | salvianolic acid B | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 121521-90-2 | Molecular Weight | 718.614 | |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 1020.3±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C36H30O16 | Melting Point | 98-110ºC | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 322.1±27.8 °C | |
Use of salvianolic acid BSalvianolic acid B is an active ingredient of Salvia miltiorrhiza, which has been widely applied in China for the management of various microcirculation-related disorders, such as cardiovascular disease, cerebrovascular disease, and diabetic vascular complication.IC50 value:Target:In vitro: Salvianolic acid B (SA-B) 1 and 10 micromol/L decrease the cell active TGF-beta1 secretion by 63.3 % and 15.6 % of the control, down-regulat pro-collgen alpha1(I) mRNA expression to 77.0% and 51.8% respectively (P<0.05). SA-B 1 and 10 micromol/L also inhibit MAPK activity by 1 to 2 fold respectively [3].In vivo: Salvianolic acid B (SalB) (5 mg · kg-1 · h-1) significantly attenuates LPS-induced pulmonary microcirculatory disturbance, including the increase in leukocyte adhesion and albumin leakage. In addition, LPS increases pulmonary tissue wet-to-dry weight ratio and tumor necrosis factor [alpha] and interleukin 8 levels in plasma and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid enhances the expression of E-selectin, intercellular adhesion molecule 1, myeloperoxidase, MMP-2, and MMP-9, whereas it decreases the expression of AQP-1 and AQP-5 in pulmonary tissue, all of which are attenuated by SalB pretreatment[1]. SalB administration (10 mg/kg) significantly ameliorate the Aβ25-35 peptide-induced memory impairment in the passive avoidance task (P<0.05). SalB treatment also reduced the number of activated microglia and astrocytes that are observed during the inflammatory reaction after the administration of the Aβ25-35 peptide. Moreover, SalB markedly reduce inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 expression levels and thiobarbituric acid reactive substances, which are increased by the administration of the Aβ25-35 peptide. Furthermore, SalB administration significantly rescue the Aβ25-35 peptide-induced decrease of choline acetyltransferase and brain-derived neurotrophic factor protein levels[2]. |
| Name | Salvianolic acid B |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Salvianolic acid B is an active ingredient of Salvia miltiorrhiza, which has been widely applied in China for the management of various microcirculation-related disorders, such as cardiovascular disease, cerebrovascular disease, and diabetic vascular complication.IC50 value:Target:In vitro: Salvianolic acid B (SA-B) 1 and 10 micromol/L decrease the cell active TGF-beta1 secretion by 63.3 % and 15.6 % of the control, down-regulat pro-collgen alpha1(I) mRNA expression to 77.0% and 51.8% respectively (P<0.05). SA-B 1 and 10 micromol/L also inhibit MAPK activity by 1 to 2 fold respectively [3].In vivo: Salvianolic acid B (SalB) (5 mg · kg-1 · h-1) significantly attenuates LPS-induced pulmonary microcirculatory disturbance, including the increase in leukocyte adhesion and albumin leakage. In addition, LPS increases pulmonary tissue wet-to-dry weight ratio and tumor necrosis factor [alpha] and interleukin 8 levels in plasma and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid enhances the expression of E-selectin, intercellular adhesion molecule 1, myeloperoxidase, MMP-2, and MMP-9, whereas it decreases the expression of AQP-1 and AQP-5 in pulmonary tissue, all of which are attenuated by SalB pretreatment[1]. SalB administration (10 mg/kg) significantly ameliorate the Aβ25-35 peptide-induced memory impairment in the passive avoidance task (P<0.05). SalB treatment also reduced the number of activated microglia and astrocytes that are observed during the inflammatory reaction after the administration of the Aβ25-35 peptide. Moreover, SalB markedly reduce inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 expression levels and thiobarbituric acid reactive substances, which are increased by the administration of the Aβ25-35 peptide. Furthermore, SalB administration significantly rescue the Aβ25-35 peptide-induced decrease of choline acetyltransferase and brain-derived neurotrophic factor protein levels[2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 1020.3±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 98-110ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C36H30O16 |
| Molecular Weight | 718.614 |
| Flash Point | 322.1±27.8 °C |
| Exact Mass | 718.153381 |
| PSA | 278.04000 |
| LogP | 2.14 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.739 |
| InChIKey | SNKFFCBZYFGCQN-ARBMFGAVSA-N |
| SMILES | O=C(C=Cc1ccc(O)c2c1C(C(=O)OC(Cc1ccc(O)c(O)c1)C(=O)O)C(c1ccc(O)c(O)c1)O2)OC(Cc1ccc(O)c(O)c1)C(=O)O |
| Storage condition | -20°C Freezer |
| Water Solubility | H2O: ≥5mg/mL |
|
Surfactant-coated graphitized multiwalled carbon nanotubes as the pseudostationary phase in electrokinetic chromatography for the analysis of phytochemical compounds in biological fluids.
Electrophoresis 36(7-8) , 1055-63, (2015) This report describes the use of surfactant-coated graphitized multiwalled carbon nanotubes (SC-GMWNTs) as a novel pseudostationary phase in CE with diode array detection for the determination of phen... |
|
|
Tissue-smashing based ultra-rapid extraction of chemical constituents in herbal medicines
J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 95 , 213-9, (2014) Sample extraction is the first challenge in analysis of herbal medicines (HMs). Numerous methods have been developed to improve extraction efficiency, use less solvent and short time. In this work, a ... |
|
|
The caffeic acid in aqueous extract of Tournefortia sarmentosa enhances neutrophil phagocytosis of Escherichia coli.
Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 36(6) , 390-6, (2014) Tournefortia sarmentosa, a Chinese herbal medicine, is considered an antioxidant or a detoxicating agent. Recently T. sarmentosa has received attention for its effects on the immune response. Here we ... |
| (2R)-2-({(2E)-3-[(2R,3R)-3-{[(1R)-1-Carboxy-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)ethoxy]carbonyl}-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-7-hydroxy-2,3-dihydro-1-benzofuran-4-yl]prop-2-enoyl}oxy)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)propanoic acid |
| lithospermic acid B |
| SalvianolicacidB |
| (2R)-2-({(2E)-3-[(2R,3R)-3-{[(1R)-1-Carboxy-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)ethoxy]carbonyl}-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-7-hydroxy-2,3-dihydro-1-benzofuran-4-yl]-2-propenoyl}oxy)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)propanoic acid |
| 3-Benzofurancarboxylic acid, 4-[(1E)-3-[(1R)-1-carboxy-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)ethoxy]-3-oxo-1-propen-1-yl]-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2,3-dihydro-7-hydroxy-, 3-[(1R)-1-carboxy-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)ethyl] ester, (2R,3R)- |
| salvianolic acid B |
| DanfensuanB |

