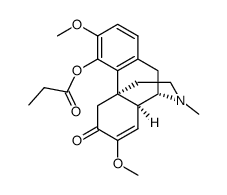
Sinomenine
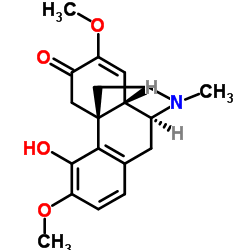
Sinomenine structure
|
Common Name | Sinomenine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 115-53-7 | Molecular Weight | 329.390 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 513.6±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C19H23NO4 | Melting Point | 180ºC | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 264.4±30.1 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of SinomenineSinomenine, an alkaloid extracted from Sinomenium acutum, is a blocker of the NF-κB activation[1]. Sinomenine also is an activator of μ-opioid receptor[2]. |
| Name | Sinomenine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Sinomenine, an alkaloid extracted from Sinomenium acutum, is a blocker of the NF-κB activation[1]. Sinomenine also is an activator of μ-opioid receptor[2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
NF-κB[1], μ-opioid receptor[2] |
| In Vitro | Cell viability gradually decreased with increasing Sinomenine concentration. The migration ability of MDA-MB-231 cells is significantly weakened by 0.25, 0.5, and 1 mM of Sinomenine treatment. The wound-healing assay reveals that 0.25 and 0.5 mM Sinomenine significantly suppress the healing of the wound. When the MDA-MB-231 cells are treated with 0.5 mM Sinomenine, the healing progress is about 50%, but in the group treated with 0.25 mM Sinomenine and the untreated control, the healing is about 80% and nearly 95%, respectively. The IB assay following inhibitor of NF-κB (IκB) antibody IP shows that the binding of NF-κB to IκB is inhibited by Sinomenine treatment in a dose-dependent manne[1]. |
| In Vivo | Sinomenine (i.p.) produces antinociception in the hot plate and tail flick tests in male rats at 40 mg/kg, but not at lower doses (10 or 20 mg/kg). At 10 to 40 mg/kg Sinomenine does not produce any observable side effect such as sedation, allergy or motor impairments. At 80 mg/kg, Sinomenine is mildly sedative in rats. Antinociception is also seen mice at 60 min following 80 mg/kg i.p. Sinomenine, but not at lower doses (20 or 40 mg/kg), in the tail flick test. Sinomenine at 80 mg/kg i.p. does not produce any observable side effects in mice. I.p or p.o. Sinomenine at 40 or 80 mg/kg dose-dependently reduces mechanical hypersensitivity in nerve injured mice. I.p. Sinomenine at 40 mg/kg, but not lower doses or vehicle, significantly decreases mechanical and cold allodynia for up to 240 min without producing motor deficits or sedation[3]. At doses of 10 to 40 mg/kg, Sinomenine dose-dependently increases the paw withdrawal threshold. In non-chronic constriction injury (CCI) healthy rats, Sinomenine at the dose range of 10 to 40 mg/kg does not change the immobility behavior in the forced swimming test[4]. |
| Cell Assay | The MDA-MB-231 human triple negative and 4T1 mouse breast cancer cell lines are used in this study. For the experiments, the cells are grown in 24-well plates at 3.5×104/well. Following incubation for 24 or 48 h in medium containing different concentrations of Sinomenine, proliferation of the cells are detected with Cell Counting Kit-8 solution according to the manufacturer's instructions[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Male Sprague-Dawley rats weighing of 250 to 300 g are used in this experiment. For the duration of action of acute Sinomenine study, different doses of Sinomenine (10 to 40 mg/kg) are administered 1 day after surgery and then paw withdrawal threshold is measured every 30 min for 4 hours. For the study involving daily Sinomenine treatment, mechanical hyperalgesia measure is performed 3 h after daily drug treatment. For antagonist studies, antagonists were given 10 min prior to 40 mg/kg Sinomenine administration[3]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 513.6±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 180ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C19H23NO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 329.390 |
| Flash Point | 264.4±30.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 329.162720 |
| PSA | 59.00000 |
| LogP | 1.25 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.625 |
| Storage condition | 2~8°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P301 + P312 + P330-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Hazard Codes | T: Toxic; |
| Risk Phrases | R45 |
| Safety Phrases | 53-22-26-36/37/39-45 |
| RIDADR | UN 1544 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | QD2170000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(b) |
|
~10% 
Sinomenine CAS#:115-53-7 |
| Literature: Cui, Xiaoxue; Li, Bo; Liu, Tianzhen; Li, Chunbao Green Chemistry, 2012 , vol. 14, # 3 p. 668 - 672 |
|
~99% 
Sinomenine CAS#:115-53-7 |
| Literature: Cui, Xiaoxue; Li, Bo; Liu, Tianzhen; Li, Chunbao Green Chemistry, 2012 , vol. 14, # 3 p. 668 - 672 |
| Precursor 1 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
|
[Research advances of mechanism of sinomenine in treating rheumatoid arthritis].
Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao 7(8) , 775-8, (2009)
|
|
|
[New study progress of sinomenine].
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 30(20) , 1573-6, (2005) To further understand sinomenine, this paper has introduced the abstract technology, assaying, pharmaceutical chemistry, pharmacological action, pharmacotoxicology, pharmacokinetics and clinical appli... |
|
|
Immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory activities of sinomenine.
Int. Immunopharmacol. 11(3) , 373-6, (2011) Sinomenine (SN), a pure compound extracted from the Sinomenium acutum plant, has been found to inhibit T- and B-lymphocyte activation, proliferation and function and to interfere with the differentiat... |
| EINECS 204-094-6 |
| MFCD00134303 |