Minocycline
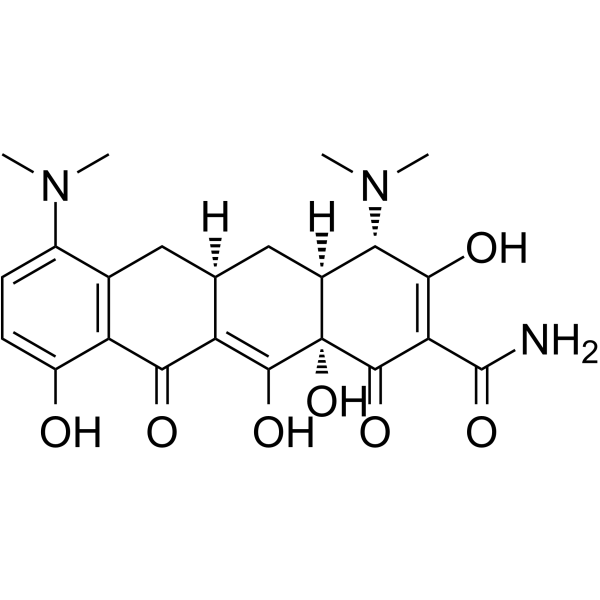
Minocycline structure
|
Common Name | Minocycline | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 10118-90-8 | Molecular Weight | 457.476 | |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 803.3±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C23H27N3O7 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 439.6±34.3 °C | |
Use of MinocyclineMinocycline is an orally active, potent and BBB-penetrated semi-synthetic tetracycline antibiotic. Minocycline is a hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α inhibitor. Minocycline shows anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, and glutamate antagonist effects. Minocycline reduces glutamate neurotransmission and shows neuroprotective properties and antidepressant effects. Minocycline inhibits bacterial protein synthesis through binding with the 30S subunit of the bacterial ribosome, resulting in a bacteriostatic effect[1][2][3][4][5][6][7]. |
| Name | minocycline |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Minocycline is an orally active, potent and BBB-penetrated semi-synthetic tetracycline antibiotic. Minocycline is a hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α inhibitor. Minocycline shows anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, and glutamate antagonist effects. Minocycline reduces glutamate neurotransmission and shows neuroprotective properties and antidepressant effects. Minocycline inhibits bacterial protein synthesis through binding with the 30S subunit of the bacterial ribosome, resulting in a bacteriostatic effect[1][2][3][4][5][6][7]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
L-type calcium channel |
| In Vitro | Minocycline (0-100 μM, 24-72 h) suppresses proliferation and clonogenic activity of ovarian cancer cell-lines (OVCAR-3, SKOV-3 and A2780)[3]. Minocycline (0-100 μM, 24-48 h)arrests cell cycle through inhibition of cyclins and suppression of DNA incorporation[3]. Minocycline (0-100 μM, 72 h) induces cell apoptosis in ovarian cancer cell lines[3]. Minocycline shows direct neuronal protection, and this mode of protection is likely to be associated with the preservation of mitochondrial integrity and cytochrome c, followed by the suppression of caspase-dependent as well as caspase-independent cell death[2]. Minocycline leads to suppression of Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α accompanied by up-regulation of p53 protein levels and inactivation of AKT/mTOR/p70S6K/4E-BP1 pathway[6]. Cell Proliferation Assay[3] Cell Line: Human ovarian cancer cell lines (OVCAR-3, SKOV-3 and A2780) and primary cells (HEK-293, HMEC, HUVEC, ATCC) Concentration: 0, 1, 10, 50 and 100 μM Incubation Time: 24, 48 or 72 h Result: Inhibited proliferation of OVCAR-3, SKOV-3 and A2780 cells in a concentration-dependent manner, with IC50 values of 62.0, 56.1 and 59.5 μM, respectively. Had no effect on the viability of HEK-293 or HUVEC. Cell Cycle Analysis[3] Cell Line: OVCAR-3, SKOV-3 and A2780 cells Concentration: 0, 10, 50 and 100 μM Incubation Time: 24 or 48 h Result: Arrested cells in the G0-G1 phase in a concentration and time-dependent manner. Declined percentage of cells in the S and G2-M phases in excess of 80% each at 100 μM. Western Blot Analysis[3] Cell Line: OVCAR-3, SKOV-3 and A2780 cells Concentration: 0, 10, 50 and 100 μM Incubation Time: 72 h Result: Expressed lower levels of cyclins A, B and E. Increased caspase-3 levels by more than 3.0 fold in the 100 μM. Minocycline-activated caspase-3 in turn led to cleavage of PARP-1. Increased the degradation product p89 of PARP-1 by caspase-3. |
| In Vivo | Minocycline (0-30 mg/kg, orally, daily for 4 weeks) suppresses OVCAR-3 tumor growth in female nude mice[3]. Minocycline (IP) is an effective neuroprotective agent in animal models of cerebral ischemia when given in high doses intraperitoneally[1]. Minocycline (0-40 mg/kg, IP, once) significantly attenuats METH-induced hyperlocomotion and the development of behavioral sensitization in mice[2]. Minocycline (3 and 10 mg/kg, IV, once) is effective at reducing infarct size in a Temporary Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion model (TMCAO)[1]. Minocycline (3-10 mg/kg, IV, once) results in serum levels (at 3 mg/kg) similar to that achieved in humans after a standard 200 mg dose[1]. Minocycline attenuates ischemia-induced ventricular arrhythmias in rats. This effect may be associated with activations of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway, mitochondrial KATP channels and L-type Ca2+ channels[7]. Animal Model: Female nude mice (6 weeks old, 9 per group, OVCAR-3 cells were injected s.c. into the left flank of each mouse)[3] Dosage: 10 or 30 mg/kg Administration: Administered orally in the drinking water, initiated on day 8 of cell inoculation, daily for 4 weeks Result: Suppressed OVCAR-3 tumor growth in these female nude mice, and reduced microvessel density. Animal Model: Male Balb/cAnNCrICrIj mice (8 weeks old, 23-30 g, methamphetamine (METH, 3 mg/kg) was injected subcutaneously (s.c.) in a volume of 10 ml/kg)[2] Dosage: 0, 10, 20, or 40 mg/kg Administration: IP, once, 30 min before the administration of METH Result: Significantly attenuated METH-induced hyperlocomotion and the development of behavioral sensitization in mice at 40 mg/kg. Did not exert any effect on the induction of METH-induced hyperthermia in mice. Significantly attenuated the reduction of DA and DOPAC in the striatum. Significantly attenuated the reduction of DAT-immunoreactivity in the mouse striatum. Significantly attenuated the increase in MAC1-immunoreactivity in the striatum after the administration of METH. Animal Model: Male Sprague-Dawley rats (270-330 g, TMCAO model)[1] Dosage: 3 mg/kg and 10 mg/kg Administration: IV, once, 4, 5, or 6 hours post TMCAO Result: Reduced infarct size by 42% while 10 mg/kg reduced infarct size by 56% at doses of 3 mg/kg; significantly reduced infarct size at 5 hours by 40% at doses of 10 mg/kg and the 3 mg/kg dose significantly reduced infarct size by 34%. With a 6 hour time window there was a non-significant trend in infarct reduction. Animal Model: Male Sprague-Dawley rats (270-330 g)[1] Dosage: 3, 10, or 20 mg/kg Administration: IV, once Result: Peak concentrations of serum levels of minocycline averaged 3.6, 13.0 and 28.8 mg/L with 3, 10 and 20 mg/kg doses respectively. The serum levels of minocycline at a 3 mg/kg dose (3.6 mg/L) were similar to that reported in humans after a standard 200 mg dose. Did not significantly affect hemodynamic and physiological variables. |
| References |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 803.3±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C23H27N3O7 |
| Molecular Weight | 457.476 |
| Flash Point | 439.6±34.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 457.184906 |
| PSA | 164.63000 |
| LogP | -0.65 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.718 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
|
~% 
Minocycline CAS#:10118-90-8 |
| Literature: WO2010/33939 A1, ; Page/Page column 36 ; |
|
~66% 
Minocycline CAS#:10118-90-8 |
| Literature: The Journal of organic chemistry, , vol. 67, # 14 p. 5025 - 5027 |
| (4S,4aS,5aR,12aS)-4,7-Bis(dimethylamino)-3,10,12,12a-tetrahydroxy-1,11-dioxo-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydro-2-tetracenecarboximidic acid |
| Minocyclin |
| Minocin |
| 7-dimethylamino-6-demethyl-6-deoxytetracycline |
| (4S,4aS,5aR,12aS)-4,7-Bis(dimethylamino)-3,10,12,12a-tetrahydroxy-1,11-dioxo-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydro-2-tetracenecarboxamide |
| 4S-(4a,4aa,5aa,12aa)-4,7-bis(dimethylamino)-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydro-3,10,12,12a-tetrahydroxy-1,11-dioxo-2-naphthacene carboxamide |
| Minocyclinum |
| [4S-(4a,4aa,5aa,12aa)]-4,7-Bis(dimethylamino)-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydro-3,10,12,12a-tetrahydroxy-1,11-dioxo-2-naphthacenecarboxamide |
| 2-Naphthacenecarboximidic acid, 4,7-bis(dimethylamino)-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydro-3,10,12,12a-tetrahydroxy-1,11-dioxo-, (4S,4aS,5aR,12aS)- |
| Apo-Minocycline |
| (4S,4aS,5aR,12aR)-4,7-bis(dimethylamino)-1,10,11,12a-tetrahydroxy-3,12-dioxo-4a,5,5a,6-tetrahydro-4H-tetracene-2-carboxamide |
| (4S,4aS,5aR,12aS)-4,7-bis(dimethylamino)-3,10,12,12a-tetrahydroxy-1,11-dioxo-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydrotetracene-2-carboxamide |
| 2-Naphthacenecarboxamide, 4,7-bis(dimethylamino)-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydro-3,10,12,12a-tetrahydroxy-1,11-dioxo-, (4S,4aS,5aR,12aS)- |
| Minocycline |
| Arestin |
| 7-(N,N-dimethylamino)sancycline |
| Aknemin |
| Minocyclinum [INN-Latin] |
| EINECS 237-099-7 |
| Dynacin |
| Minociclina |
| MFCD00083669 |
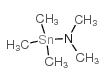

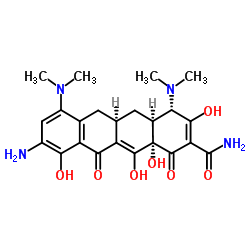 CAS#:149934-19-0
CAS#:149934-19-0