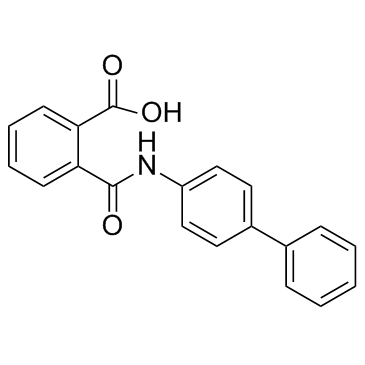
4727-31-5
| Name | 2-[(4-phenylphenyl)carbamoyl]benzoic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
2-[([1,1'-biphenyl]-4-ylamino)carbonyl]benzoic acid
Kartogenin 2-([1,1'-Biphenyl]-4-ylcarbamoyl)benzoic acid 2-(4-Biphenylylcarbamoyl)benzoic acid 2-(Biphenyl-4-ylcarbamoyl)benzoic acid KGN |
| Description | Kartogenin is an inducer of differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells into chondrocytes. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Kartogenin enhances cell proliferation in both cell types in a concentration-dependent manner and induces chondrogenic differentiation of stem cells, as demonstrated by high expression levels of chondrogenic markers aggrecan, collagen II and Sox-9. Besides, kartogenin induces the formation of cartilage-like tissues in cell cultures, as observed through the staining of abundant proteoglycans, collagen II and osteocalcin[1]. Kartogenin stimulates type-I collagen synthesis of fibroblasts at the mRNA and protein levels in a time-dependent manner without obvious influence on fibroblasts’ apoptosis and viability. Smad4/smad5 of the TGF-β signaling pathway is activated by kartogenin while MAPK signaling pathway remains unchanged[2]. Kartogenin treatment enhances chondrocyte pericellular matrix assembly and retention in the presence of IL-1β. Kartogenin partially blocks the IL-1β-induced increased expression of ADAMTS-5. Additionally, kartogenin-treated articular chondrocytes exhibits a decrease in CD44 proteolytic fragmentation[3]. |
| In Vivo | hen injected into intact rat patellar tendons, kartogenin induces cartilage-like tissue formation in the injected area. When injected into experimentally injured rat Achilles TBJs, wound healing in the TBJs is enhanced, as evidenced by the formation of extensive cartilage-like tissues[1]. Kartogenin stimulates collagen synthesis in the mouse dermis. Dermis in the kartogenin (100 nM)-treated group exhibits increased dermal thickness and intense blue staining, which represents more collagen composition in the dermis[2]. |
| Cell Assay | Rabbit BMSCs or PTSCs are treated with various concentrations (1 nM to 5 μM) of kartogenin. The medium is changed every 3 days and after 2 weeks, cell proliferation is measured by population doubling time[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Rats: Then rats are divided into two groups based on the injections received: six rats are given 10 µL saline injections in each wound (wound-only group) and six rats receive 10 µL of 100 µM kartogenin solution each in the wounded areas (wound+kartogenin group). The injections are given immediately after wounding and repeated on days 2, 4, 7 and 12[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 464.4±38.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C20H15NO3 |
| Molecular Weight | 317.338 |
| Flash Point | 234.6±26.8 °C |
| Exact Mass | 317.105194 |
| PSA | 66.40000 |
| LogP | 3.81 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.674 |
| Storage condition | room temp |
| Water Solubility | DMSO: >15mg/mL |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H319-H410 |
| Precautionary Statements | P273-P305 + P351 + P338-P501 |
| Hazard Codes | Xn,N |
| Risk Phrases | 22-36-50/53 |
| Safety Phrases | 60-61 |
| RIDADR | UN 3077 9 / PGIII |
| Hazard Class | 9.0 |
| HS Code | 2924299090 |
| HS Code | 2924299090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2924299090. other cyclic amides (including cyclic carbamates) and their derivatives; salts thereof. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |