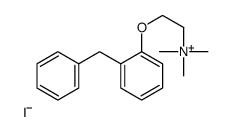
92-12-6
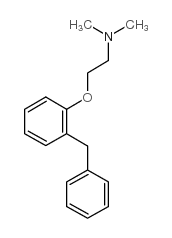
| Name | 2-(2-benzylphenoxy)-N,N-dimethylethanamine |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Feniltolossamina [DCIT]
Phenyltoloxamine Phenoxadrine Antin [2-(2-benzyl-phenoxy)-ethyl]-dimethyl-amine Histionex 2-Dimethylamino-1-(2-benzyl-phenoxy)-aethan Bistrimin Phenoxadrin UNII-K65LB6598J Phenyl-toloxamin Phentoloxamine Bristamin [2-(2-Benzyl-phenoxy)-aethyl]-dimethyl-amin |
| Description | Phenyltoloxamine (Bistrimin) is an antihistamine agent with sedative and analgesic effects. Phenyltoloxamine also has potent Sigma-1 receptor binding affinity (Ki: 160 nM)[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Sigma 1 Receptor:160 nM (Ki) |
| In Vitro | Phenyltoloxamine (10-50 μM, 24 h) demonstrates cytotoxicity in EVSA-T cells[2]. Phenyltoloxamine exhibits potent Sigma 1 Receptor (S1R) binding affinity with a Ki value of 160 nM[3]. Phenyltoloxamine (100 μM) inhibits human liver macrosaml CYP2D6 enzyme by 99.0%[4]. |
| Density | 1.022g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 359.2ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C17H21NO |
| Molecular Weight | 255.35500 |
| Flash Point | 106ºC |
| Exact Mass | 255.16200 |
| PSA | 12.47000 |
| LogP | 3.21780 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.552 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
|
~% 
92-12-6 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 47, # 17 p. 4155 - 4158 |
|
~% 
92-12-6 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 24, # 2 p. 145 - 148 |
|
~% 
92-12-6 |
| Literature: Journal of the American Chemical Society, , vol. 71, p. 60,62 |
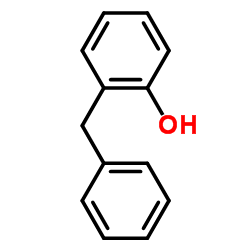
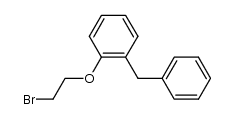
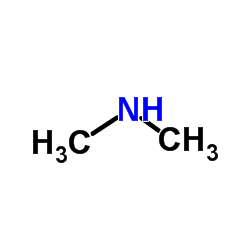
| Precursor 5 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |