167465-36-3
| Name | Zosuquidar Trihydrochloride |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
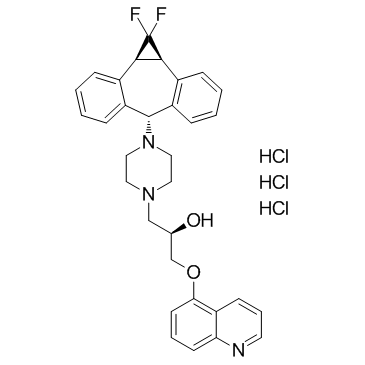
(R)-4-[(1aR,6R,10bS)-1,2-difluoro-1,1a,6,10b-tetrahydrodibenzo[a,e]cyclopropa[c]cycloheptan-6-yl]-α-[(5-quinoloyloxy)methyl]-1-piperazineethanol trihydrochloride
Zosuquidar Trihydrochloride 1-Piperazineethanol, 4-[(1aR,10bS)-1,1-difluoro-1,1a,6,10b-tetrahydrodibenzo[a,e]cyclopropa[c]cyclohepten-6-yl]-α-[(5-quinolinyloxy)methyl]-, (αR)-, hydrochloride (1:3) (2R)-1-{4-[(1aR,10bS)-1,1-Difluoro-1,1a,6,10b-tetrahydrodibenzo[a,e]cyclopropa[c][7]annulen-6-yl]-1-piperazinyl}-3-(5-quinolinyloxy)-2-propanol trihydrochloride LY335979 Zosuquidar 3HCl Zosuquidar (trihydrochloride) |
| Description | Zosuquidar trihydrochloride is an inhibitor of P-glycoprotein with a Ki value of 59 nM. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Ki: 59nM (P-glycoprotein)[1]. |
| In Vitro | Zosuquidar completely or partially restores drug sensitivity in all P-gp-expressing leukemia cell lines and enhances the cytotoxicity of anthracyclines (daunorubicin, idarubicin, mitoxantrone) and gemtuzumab ozogamicin (Mylotarg) in primary AmL blasts with active P-gp. In addition, P-gp inhibition by zosuquidar is found to be more potent than cyclosporine A in cells with highly active P-gp[2]. |
| In Vivo | Zosuquidar trihydrochloride is only moderately active as an inhibitor of P-gp at the blood-brain. An oral dose of 25 mg/kg of zosuquidar trihydrochloride increases the brain concentrations by about 2.5-fold at 1 h and 5-fold at 24 h after paclitaxel administrationbarrier[3]. Zosuquidar enhances the brain uptake of nelfinavir in a dose-dependent manner. Brain tissue/plasma nelfinavir concentration ratios increase from 0.06±0.03 in the absence of zosuquidar administration and 0.09±0.02 between 2 and 6 h after a 2 mg/kg intravenous dose of zosuquidar to 0.85±0.19 after 6h and 1.58±0.67 after 20 mg/kg zosuquidar[4]. |
| Cell Assay | Cells are cultured in 96-well plates. Each drug of interest is added at escalating concentrations in the presence or absence of either zosuquidar or CsA. After 48 hour incubation (except Mylotarg, 4 days incubation), 20 μL of MTT is added to each well for a further 4 hour incubation. The purple precipitate is dissolved in 200 μL DMSO, and the optic density (OD) is determined by the multi-well plate reader[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Rats: Female Sprague-Dawley rats are used in the study. Zosuquidar solutions are prepared in 5% mannitol and adjusted to pH ~2.0 with concentrated HCl. Nelfinavir is infused (10 mg/kg/h) for up to 10 h with or without concurrent administration of an intravenous bolus dose of 2, 6, or 20 mg/kg zosuquidar given at 4 h. Brain tissue and plasma are analyzed for both drug concentrations[4]. Mice: A stock solution of 5 mg/mL of zosuquidar trihydrochloride is prepared in vehicle solution and diluted in sterile saline. The vehicle solution consisted of 20 g/l mannitol and 1.5 g/l of glycine in water for injection and adjusted to a pH of 2.7 with hydrochloric acid. P-gp knockout mice and wild type mice are used as a model for complete inhibition of P-gp. Zosuquidar trihydrochloride is administered orally at 25 and 80 mg/kg 1 h before i.v. paclitaxel and i.v. at 20 mg/kg 10 min and 1 h before paclitaxel. The concentrations of paclitaxel in plasma and tissues and of zosuquidar trihydrochloride in plasma are quantified by high-performance liquid chromatography[3]. |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 690.5ºC at 760mmHg |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 172-176°C |
| Molecular Formula | C32H34Cl3F2N3O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 636.987 |
| Flash Point | 371.4ºC |
| Exact Mass | 635.168457 |
| PSA | 48.83000 |
| LogP | 7.49320 |
| Storage condition | Hygroscopic, -20?C Freezer, Under Inert Atmosphere |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|