22910-60-7
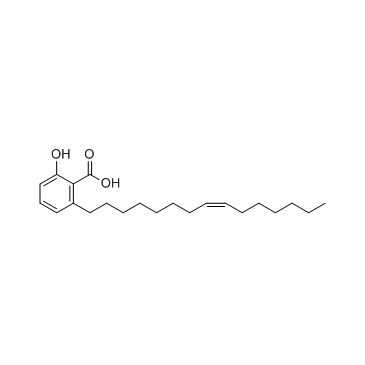
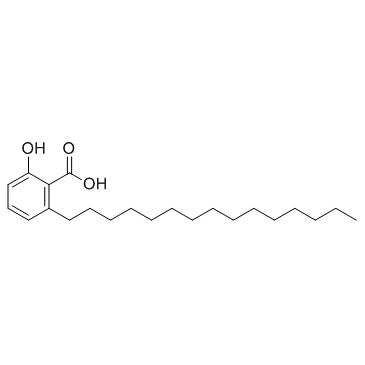
| Name | 2-hydroxy-6-[(Z)-pentadec-8-enyl]benzoic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
MFCD03093717
15:1 anacardic acid Ginkgolic acid Ginkgolic acid 15:1 Romanicardic acid (Z)-2-Hydroxy-6-(pentadec-8-en-1-yl)benzoic acid Ginkgolic acid (15:1) 2-Hydroxy-6-(pentadec-8-en-1-yl)benzoic acid (Z)-6-[8-pentadecenyl]salicylic acid 2-hydroxy-6-pentadec-8(Z)-enylbenzoic acid 6-[(8Z)-Pentadecenyl]-salicylic acid,Ginkgolic acid I Ginkgoic acid 2-hydroxy-6-(8-pentadecenyl) salicylic acid Anacardic acid monoene 6-(8-pentadecenyl)salicylic acid 2-Hydroxy-6-[(8Z)-pentadec-8-en-1-yl]benzoic acid Ginkgolic acid I Gingkolic Acid 2-Hydroxy-6-[(8Z)-8-pentadecen-1-yl]benzoic acid 6-(8Z-pentadecenyl)salicylic acid Ginkgolic acid (C15:1) 6-<8(Z)-pentadecenyl>salicylic acid Ginkgolic Acid C15:1 (Z)-2-Hydroxy-6-(8-pentadecenyl)benzoic acid |
| Description | Ginkgolic Acid is a natural compound with suspected cytotoxic, allergenic, mutagenic and carcinogenic properties, and it can inhibit protein SUMOylation both in vitro and in vivo without affecting in vivo ubiquitination. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Ginkgolic acid inhibits the in vitro SUMOylation of RanGAP1-C2 with the IC50 values of 3.0 μM. The level of SUMOylated p53 is markedly reduced by the ginkgolic acid treatment. Importantly, ginkgolic acid does not affect protein ubiquitination in cells. Ginkgolic acid inhibits the binding between E1 and GA-BODIPY in a dose-dependent manner[1]. Ginkgolic acid (31.2 μg/mL) inhibits HIV protease activity by 60%, compared with the negative control, and the effect is concentration-dependent. Ginkgolic acid treatment (50 and 100 μg/mL) effectively inhibits HIV infection in human PBMC cells. Ginkgolic acid at the concentrations up to 150 μg/mL does not cause any significant cytotoxicity in Jurkat cells[2]. GA only inhibits the growth of tumorogenic cell lines in a both dose- and time-dependent manner. Tumor cells are treated with GA for 72 h, 70.53±4.54% Hep-2 and 63.5±7.2% Tca8113 cells are retarded at GO/G1 phase, and the percentage of apoptosis is 40.4±1.58 and 38.4±1.7%, respectively. GA-treated activated caspase-3 downregulates the expression of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 protein and upregulates the expression of pro-apoptotic Bax protein, eventually leading to a decrease in the Bcl-2/Bax ratio in tumor cellsin human PBMC cells. Ginkgolic acid at the concentrations up to 150 μg/mL does not cause any significant cytotoxicity in Jurkat cells[3]. |
| Cell Assay | Jurkat cells (106 cells/mL) are cultured in the RPMI medium with or without different concentrations of ginkgolic acid for 48 hours to test the cytotoxicity of ginkgolic acid. The cytotoxicity of ginkgolic acid is determined using a tetrazolium compound (MTS) and an electron coupling reagent (PMS). MTS is chemically reduced by cells into formazan, which is soluble in the tissue culture medium. The measurement of the absorbance of the formazan can be carried out using 96 well microplates at 492 nm. Since the production of formazan is proportional to the number of living cells, the intensity of the produced color is a good indication of the viability of the cells. |
| References |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 492.1±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 136-137ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C22H34O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 346.504 |
| Flash Point | 265.5±23.8 °C |
| Exact Mass | 346.250793 |
| PSA | 57.53000 |
| LogP | 9.44 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.527 |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
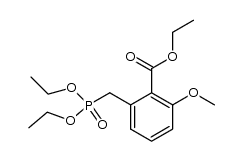
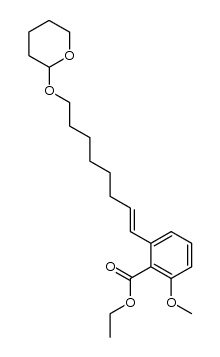
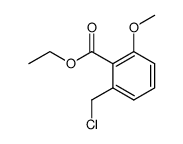
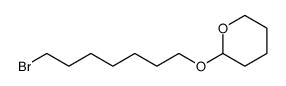
| Precursor 8 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 4 | |