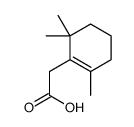
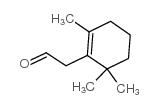
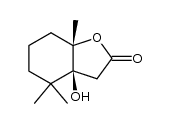
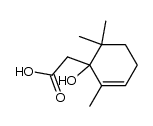
15356-74-8
| Name | Dihydroactinidiolide |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
dihydroactinidiolide
T56 BVO AH&TJ A1 F1 F1 2-Hydroxy-2,6,6-trimethylcyclohexylideneacetic acid γ-lactone 5,6,7,7a-Tetrahydro-4,4,7a-trimethyl-2(4H)-benzofuranone (±)-(2,6,6,-Trimethyl-2-hydroxycyclohexylidene)acetic acid γ-lactone 4,4,7a-Trimethyl-5,6,7,7a-tetrahydrobenzofuran-2(4H)-one 4,4,7a-Trimethyl-5,6,7,7a-tetrahydro-1-benzofuran-2(4H)-one UNII:BH8469LVA9 (7aS)-4,4,7a-Trimethyl-5,6,7,7a-tetrahydro-1-benzofuran-2(4H)-one |
| Description | (±)-Dihydroactinidiolide, an important aroma compound of black tea and tobacco, has been isolated from several plants. (±)-Dihydroactinidiolide can be formation from β-Carotene by the treatment of polyphenoloxidase, the lipoxygenase, and the xanthine oxidase[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 296.1±9.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 42-43° |
| Molecular Formula | C11H16O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 180.243 |
| Flash Point | 120.2±16.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 180.115036 |
| PSA | 26.30000 |
| LogP | 2.26 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.504 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|
| Precursor 8 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |