158930-17-7
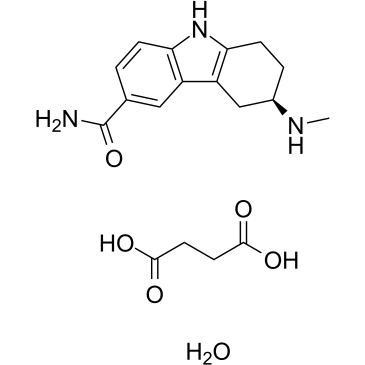
| Name | butanedioic acid,(6R)-6-(methylamino)-6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-5H-carbazole-3-carboxamide,hydrate |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
(R)-(+)-6-carbamoyl-N-methyl-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazol-3-aminium 3-carboxypropanoate monohydrate
(+)-(R)-2,3,4,9-Tetrahydro-3-(methylamino)-1H-carbazole-6-carboxamide butanedioate (1:1),monohydrate (+)-(R)-5,6,7,8-Tetrahydro-6-(methylamino)carbazole-3-carboxamide succinate (1:1),monohydrate Frovatriptan succinate [USAN] Frovatriptan Succinate monohydrate UNII-D28J6W18HY Frovatriptan succinate hydrate 1H-Carbazole-6-carboxamide,2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-3-(methylamino)-,(R)-,butanedioate (1:1),monohydrate (R)-frovatriptan succinate monohydrate |
| Description | Frovatriptan succinate hydrate is a potent, high affinity, selective and orally active 5-HT1B, HT1D receptor agonist and a moderately potent 5-HT7 receptor agonist, with pKi values of 8.6, 8.4, and 6.7, respectively. Frovatriptan succinate hydrate is effective in treating the full spectrum of migraine including the associated symptoms of nausea, vomiting, photophobia, and phonophobia. Frovatriptan succinate hydrate can also be used as in mini-prophylaxis in menstrual migraine[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
5-HT1B Receptor:8.6 (pKi) 5-HT1D Receptor:8.4 (pKi) Human 5-HT7 Receptor:6.7 (pKi) |
| In Vitro | Cerebral vasodilatation and neurogenic inflammation are considered to be prime movers in the pathogenesis of migraine. Activation of 5-HT1B reverses cerebral vasodilatation and activation of 5-HT1D prevents neurogenic inflammation. Frovatriptan has a high affinity for 5-HT1B and 5-HT1D receptors and a moderate affinity for the 5-HT1A and 5-HT1F receptors subtypes. Frovatriptan has a moderate affinity for the 5-HT7 receptors, an action associated with coronary artery relaxation in the dog[1]. |
| In Vivo | Oral bioavailability of Frovatriptan is 22%-30% and is not affected by food. Although the maximum concentration in the plasma is achieved in 2-3 hours, 60%-70% of this is achieved in 1 hour. A steady state is achieved in 4-5 days. Plasma protein binding is low at 15%. The most unique feature is the relative terminal long half-life of about 26 hours. Frovatriptan is chiefly metabolized by CYP1A2 and is cleared by the kidney and liver making moderate failure of either organ not a limiting factor in treatment. Frovatriptan has a low risk of interactions with other drugs[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.27g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 515.2ºC at 760mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C18H25N3O6 |
| Molecular Weight | 379.40800 |
| Flash Point | 265.4ºC |
| Exact Mass | 379.17400 |
| PSA | 154.74000 |
| LogP | 2.30620 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|---|