864084-88-8
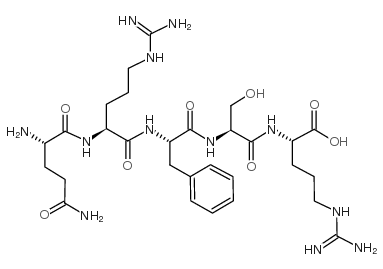
| Name | Opiorphin |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
human opiorphin
H-Gln-Arg-Phe-Ser-Arg-OH |
| Description | Opiorphin, an opioid peptide, is a potent enkephalin-inactivating zinc ectopeptidases in human inhibitor. Opiorphin inhibits two enkephalin-catabolizing ectoenzymes, human neutral ecto-endopeptidase, hNEP (EC 3.4.24.11) with an IC50 value of 11 μM, and human ecto-aminopeptidase, hAP-N (EC 3.4.11.2). Opiorphin displays potent analgesic activity by activating endogenous opioid-dependent transmission[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Opiorphin (1-100 μM; the mouse isolated colon) causes contractile effects in mouse distal colon in a concentration-dependent manner and enhances the contractile response induced by Met-enkephalin[1]. Opiorphin (0-50 μM; hNEP or hAP-N transformed HEK293 cell line) is a dual inhibitor of enkephalin-degrading hNEP and hAP-N in vitro. Opiorphin inhibits Mca-BK2 endoproteolysis by the cell-surface recombinant hNEP with an IC50 value of 33 μM. and inhibits the Ala-pNA cleavage by hAP-N with an IC50 value of 65 μM[2]. |
| In Vivo | Opiorphin (1.25-10 μg/kg; ICV; 0-60 min; male Kunming mice) induces potent analgesic effect in a dose- and time-dependent manner (ED50=3.22 μg/kg)[1]. Animal Model: Male Kunming mice[1] Dosage: 1.25, 2.5, 5, 10 μg/kg Administration: Intracerebroventrical injection; post-drug latency measurements were performed at 5, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 and 60 min Result: Had the percentage change of tail withdrawal latency (TWL) at 10 min after i.c.v. administration of 1.25-10 mg/kg was 28.90%, 44.37%, 56.43% and 91.899.79%, respectively. |
| Molecular Formula | C29H48N12O8 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 692.76700 |
| Exact Mass | 692.37200 |
| PSA | 366.84000 |
| LogP | 0.71060 |