29883-15-6
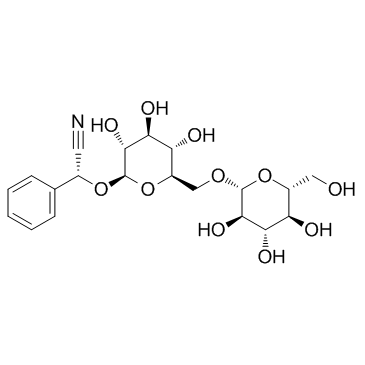
| Name | Amygdalin |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Mandelonitrile b-Glucuronide
Vitamin B17 rile (2R)-{[6-O-(β-D-Glucopyranosyl)-β-D-glucopyranosyl]oxy}(phenyl)acetonitrile Mygdalin D-amygdalin EINECS 249-925-3 (2R)-Phenyl{[(2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-({[(2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy}methyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy}acetonitrile Mandelonitrile-b-gentiobioside amygdaloside D-Mandelonitrile 6-O-β-D-glucosido-β-D-glucoside (2R)-{[6-O-(β-D-glucopyranosyl)-β-D-glucopyranosyl]oxy}(phenyl)ethanenitrile D-AMYGLADIN D-Mandelonitrile-β-gentiobioside Laetrile Nitrilosides mandelonitrile-β-gentiobioside (R)-amygdalin D-Mandelonitrile-b-D-glucosido-6-b-D-glucoside [(6-O-b-D-Glucopyranosyl-b-D-glucopyranosyl)oxy]benzeneacetonitrile Amygdalin MFCD00006598 |
| Description | Amygdalin is a plant glucoside isolated from the stones of rosaceous fruits, such as apricots, peaches, almond, cherries, and plums. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Amygdalin has antitumor activity. Some advances had been made on the antitumor mechanism of amygdalin[1]. Amygdalin downregulates especially genes belonging to cell cycle category: exonuclease 1, ATP-binding cassette, sub-family F, member 2, MRE11 meiotic recombination 11 homolog A, topoisomerase (DNA) I, and FK506 binding protein 12-rapamycin-associated protein 1. RT-PCR analysis reveals that mRNA levels of these genes are also decreased by amygdalin treatment in SNU-C4 human colon cancer cells[2]. |
| In Vivo | Amygdalin is effective at alleviating inflammatory pain and that it can be used as an analgesic with anti-nociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities. The intramuscular injection of amygdalin significantly reduced the formalin-induced tonic pain in both early (the initial 10 min after formalin injection) and late phases (10-30 min following the initial formalin injection). During the late phase, amygdalin reduces the formalin-induced pain in a dose-dependentmanner in a dose range less than 1 mg/kg[3]. |
| Cell Assay | Cell viability is determined by MTT assay. Cells are seeded in triplicate at a concentration of 1×105 cells/well on a 96-well plate. SNU-C4 cells are treated with amygdalin at concentrations of 0.25, 0.5, 2.5, and 5 mg/mL for 24 h. After MTT is added to each group, the cells are incubated for 4 h. Then, they are further incubated for 1 h, including the solution in which MTT is dissolved[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Rats: The amygdalin powder is dissolved in saline and diluted with appropriate medium. Male Sprague–Dawley rats weighing 230-250 g are used for this experiment. 50mL of 5% formalin are injected to produce fomalin-induced pain in the rats. Thirty minutes before the formalin injection to induce pain, the rats are given an intramuscular injection of amygdalin solution (0.1, 0.5, 1.0, 10 mg/kg), or saline as a vehicle control[3]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 743.3±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 223-226 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C20H27NO11 |
| Molecular Weight | 457.428 |
| Flash Point | 403.3±32.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 457.158417 |
| PSA | 202.32000 |
| LogP | -0.36 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.650 |
| Water Solubility | 83 g/L (25 ºC) |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful |
| Risk Phrases | R22 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36/37/39-S45 |
| RIDADR | 2811 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | OO8450000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(b) |



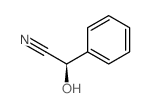
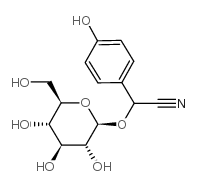
![[3,4,5-triacetyloxy-6-[[3,4,5-triacetyloxy-6-(cyano-phenyl-methoxy)oxan-2-yl]methoxy]oxan-2-yl]methyl acetate structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/094/5401-54-7.png)