114-07-8
| Name | Erythromycin |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
ROBIMYCIN
UNII-63937KV33D Theramycin Z E-BASE Inderm Erythromast 36 (3R,4S,5S,6R,7R,9R,11R,12R,13S,14R)-6-{[(2S,3R,4S,6R)-4-(Dimethylamino)-3-hydroxy-6-methyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy}-14-ethyl-7,12,13-trihydroxy-4-{[(2R,4R,5S,6S)-5-hydroxy-4-methoxy-4,6-dimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy}-3,5,7,9,11,13-hexamethyloxacyclotetradecan-2,10-dion ERYMAX Retcin Ak-Mycin Ery-Diolan Eryhexal Ery-Tab E.E.S (3R,4S,5S,6R,7R,9R,11R,12R,13S,14R)-6-{[(2S,3R,4S,6R)-4-(Dimethylamino)-3-hydroxy-6-methyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy}-14-ethyl-7,12,13-trihydroxy-4-{[(2R,4R,5S,6S)-5-hydroxy-4-methoxy-4,6-dimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy}-3,5,7,9,11,13-hexamethyloxacyclotetradecane-2,10-dione (non-preferred name) Erythromycin EMU Torlamicina (3R*,4S*,5S*,6R*,7R*,9R*,11R*,12R*,13S*,14R*)-4-((2,6-Dideoxy-3-C-methyl-3-O-methyl-α-L-ribo-hexopyranosyl)oxy)-14-ethyl-7,12,13-trihydroxy-3,5,7,9,11,13-hexamethyl-6-((3,4,6-trideoxy-3-(dimethylamino)-β-D-xylo-hexopyranosyl)oxy)oxacyclotetradecane-2,10-dione PCE MFCD00084654 Paediathrocin Erycen Erycin Erycinum ERYTHROPED Erythrogran Aknemycin Eritrocina E-MYCIN erythromycine Aknin ILOTYCIN Erythrocin Erythromid eritromicina ERYC Staticin EINECS 204-040-1 Erythroguent Ergel Estomicina Stiemycin Pharyngocin Erythromycin A USP Dotycin EMGEL (3R,4S,5S,6R,7R,9R,11R,12R,13S,14R)-6-{[(2S,3R,4S,6R)-4-(Dimethylamino)-3-hydroxy-6-methyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy}-14-ethyl-7,12,13-trihydroxy-4-{[(2R,4R,5S,6S)-5-hydroxy-4-methoxy-4,6-dimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy}-3,5,7,9,11,13-hexamethyloxacyclotetradecane-2,10-dione knin erythromycinum |
| Description | Erythromycin, an oral macrolide antibiotic produced by Streptomyces erythreus, reversibly binds to the 50S ribosome of bacteria, and inhibits protein synthesis.Target: AntibacterialErythromycin is a macrolide antibiotic that has an antimicrobial spectrum similar to or slightly wider than that of penicillin, and is often prescribed for people who have an allergy to penicillins. For respiratory tract infections, it has better coverage of atypical organisms, including Mycoplasma and legionellosis. It was first marketed by Eli Lilly and Company, and it is today commonly known as EES (erythromycin ethylsuccinate, an ester prodrug that is commonly administered). It is also occasionally used as a prokinetic agent.Erythromycin estolate has been associated with reversible hepatotoxicity in pregnant women in the form of elevated serum glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase and is not recommended during pregnancy. Some evidence suggests similar hepatotoxicity in other populations. Erythromycin displays bacteriostatic activity or inhibits growth of bacteria, especially at higher concentrations, but the mechanism is not fully understood. By binding to the 50s subunit of the bacterial 70s rRNA complex, protein synthesis and subsequent structure and function processes critical for life or replication are inhibited. Erythromycin interferes with aminoacyl translocation, preventing the transfer of the tRNA bound at the A site of the rRNA complex to the P site of the rRNA complex. Without this translocation, the A site remains occupied and, thus, the addition of an incoming tRNA and its attached amino acid to the nascent polypeptide chain is inhibited. This interferes with the production of functionally useful proteins, which is the basis of this antimicrobial action. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 818.4±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 138-140ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C37H67NO13 |
| Molecular Weight | 733.927 |
| Flash Point | 448.8±34.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 733.461243 |
| PSA | 193.91000 |
| LogP | 2.83 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.535 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful |
| Risk Phrases | R42/43 |
| Safety Phrases | S24-S37-S45 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | KF4375000 |
| HS Code | 2941500000 |
| Precursor 6 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2941500000 |
|---|



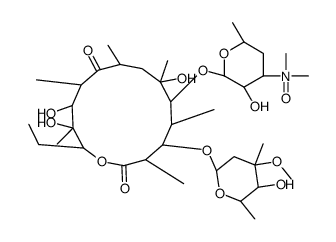
![6-O-Methyl-2',4''-bis-O-(trimethylsilyl)-9-[O-(1-ethoxy-1-methylethyl)oxime]-Erythromycin structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/142/119665-62-2.png)
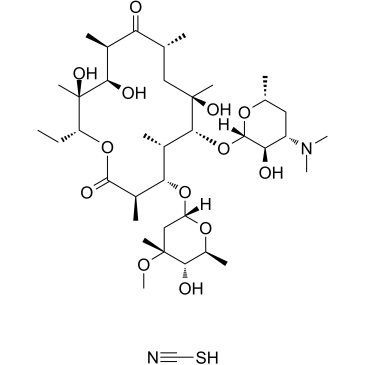

![12-[2-(dimethylamino)ethoxymethoxy]-6-[4-(dimethylamino)-3-hydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy-14-ethyl-7,13-dihydroxy-4-(5-hydroxy-4-methoxy-4,6-dimethyloxan-2-yl)oxy-10-methoxyimino-3,5,7,9,11,13-hexamethyl-oxacyclotetradecan-2-one structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/209/107749-17-7.png)