Role of postreplicative DNA mismatch repair in the cytotoxic action of thioguanine.
P F Swann, T R Waters, D C Moulton, Y Z Xu, Q Zheng, M Edwards, R Mace
Index: Science 273(5278) , 1109-11, (1996)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
It is proposed here that the delayed cytotoxicity of thioguanine involves the postreplicative DNA mismatch repair system. After incorporation into DNA, the thioguanine is chemically methylated by S-adenosylmethionine to form S6-methylthioguanine. During DNA replication, the S6-methylthioguanine directs incorporation of either thymine or cytosine into the growing DNA strand, and the resultant S6-methylthioguanine-thymine pairs are recognized by the postreplicative mismatch repair system. Azathioprine, an immunosuppressant used in organ transplantation, is partly converted to thioguanine. Because the carcinogenicity of N-nitrosamines depends on formation of O6-alkylguanine in DNA, the formation of the analog S6-methylthioguanine during azathioprine treatment may partly explain the high incidence of cancer after transplantation.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
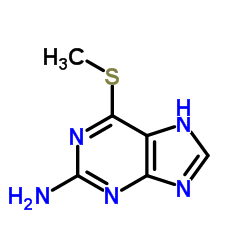 |
Purine, 2-amino-6- (methylthio)
CAS:1198-47-6 |
C6H7N5S |
|
Liquid Chromatography with Amperometric Detection at a Silve...
2015-07-07 [Anal. Chem. 87 , 6730-5, (2015)] |
|
The syntheses and properties of tricyclic pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyri...
2006-05-07 [Org. Biomol. Chem. 4(9) , 1723-9, (2006)] |
|
Reference intervals for thiopurine S-methyltransferase activ...
2004-07-01 [Ann. Clin. Biochem. 41(Pt 4) , 303-8, (2004)] |
|
Effects of various 2-amino-6-alkyldithiopurines on brain spe...
1984-06-01 [Biochem. Pharmacol. 33 , 1737-1739, (1984)] |
|
Effect of 9-alkyl derivatives of 6-methylthioguanine on brai...
1986-10-15 [Biochem. Pharmacol. 35(20) , 3645-6, (1986)] |