Reference intervals for thiopurine S-methyltransferase activity in red blood cells using 6-thioguanine as substrate and rapid non-extraction liquid chromatography.
Loretta T Ford, Sheldon C Cooper, Matthew J V Lewis, Jonathan D Berg
Index: Ann. Clin. Biochem. 41(Pt 4) , 303-8, (2004)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Although widely used, thiopurine drugs have a narrow therapeutic index and treatment can result in life-threatening toxicity, the basis being pharmacogenetic variation in thiopurine metabolism by thiopurine S-methyltransferase (TPMT). We recently developed a modified phenotyping assay to determine TPMT activity in red blood cells. Here we describe improvements to the method and establish reference intervals in a large prospective study.A modified enzyme assay for TPMT activity is reported. It uses 6-thioguanine as substrate with heat treatment of the incubate to stop the reaction and precipitate protein prior to high-performance liquid chromatographic (HPLC) analysis. Measurement of the reaction product, 6-methylthioguanine (6-MTG), uses HPLC with fluorimetric detection.The assay shows excellent characteristics, with clear discrimination of patients who are deficient in TPMT activity (< 5 nmol 6-MTG per g Hb per h) from heterozygotes (5-24 nmol 6-MTG per g Hb per h) and patients with normal activity (>25 nmol 6-MTG per g Hb per h).A modified TPMT assay is described which is suited for routine analysis in a regional centre. The method overcomes the need for extraction and has speeded up the chromatographic determination of 6-MTG, enabling large numbers of samples to be analysed. A prospective study of 1000 individuals has established the distribution of TPMT activity using the assay.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
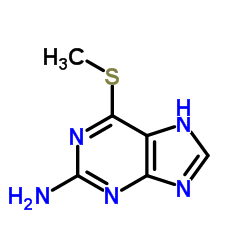 |
Purine, 2-amino-6- (methylthio)
CAS:1198-47-6 |
C6H7N5S |
|
Liquid Chromatography with Amperometric Detection at a Silve...
2015-07-07 [Anal. Chem. 87 , 6730-5, (2015)] |
|
The syntheses and properties of tricyclic pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyri...
2006-05-07 [Org. Biomol. Chem. 4(9) , 1723-9, (2006)] |
|
Effects of various 2-amino-6-alkyldithiopurines on brain spe...
1984-06-01 [Biochem. Pharmacol. 33 , 1737-1739, (1984)] |
|
Role of postreplicative DNA mismatch repair in the cytotoxic...
1996-08-23 [Science 273(5278) , 1109-11, (1996)] |
|
Effect of 9-alkyl derivatives of 6-methylthioguanine on brai...
1986-10-15 [Biochem. Pharmacol. 35(20) , 3645-6, (1986)] |