| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
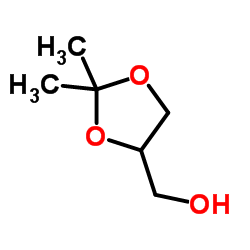 |
Solketal
CAS:100-79-8 |
|
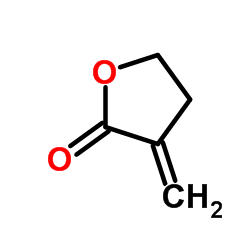 |
Tulipalin A
CAS:547-65-9 |
|
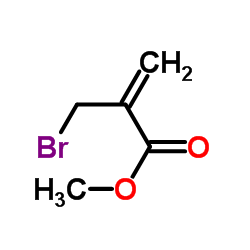 |
Methyl 2-(bromomethyl)acrylate
CAS:4224-69-5 |