| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
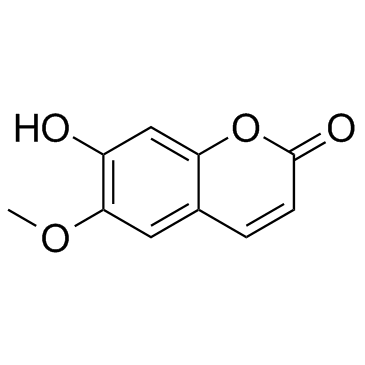 |
Scopoletin
CAS:92-61-5 |
|
 |
7-Hydroxycoumarine
CAS:93-35-6 |
|
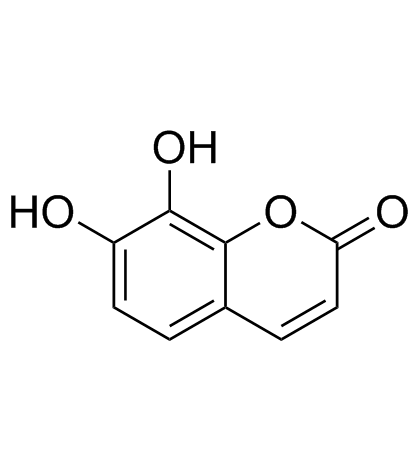 |
Daphnetin
CAS:486-35-1 |
|
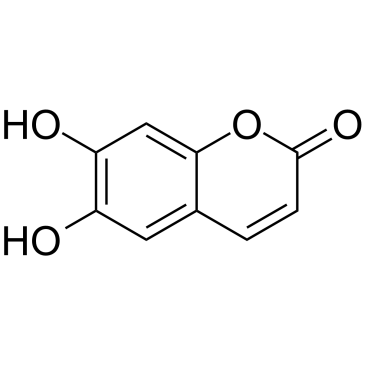 |
6,7-Dihydroxycoumarin
CAS:305-01-1 |
|
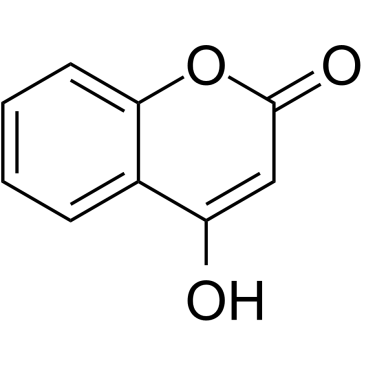 |
4-Hydroxycoumarin
CAS:1076-38-6 |