| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
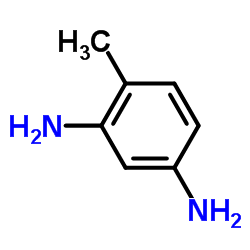 |
2,4-Diaminotoluene
CAS:95-80-7 |
|
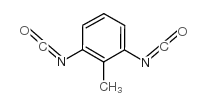 |
2-methyl-m-phenylene diisocyanate
CAS:91-08-7 |
|
 |
2,6-diaminotoluene
CAS:823-40-5 |