2,6-diaminotoluene

2,6-diaminotoluene structure
|
Common Name | 2,6-diaminotoluene | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 823-40-5 | Molecular Weight | 122.168 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 284.2±20.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C7H10N2 | Melting Point | 104-106 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 148.3±21.3 °C | |
| Symbol |



GHS07, GHS08, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
| Name | 2,6-diaminotoluene |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 284.2±20.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 104-106 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C7H10N2 |
| Molecular Weight | 122.168 |
| Flash Point | 148.3±21.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 122.084396 |
| PSA | 52.04000 |
| LogP | 0.15 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.636 |
| InChIKey | RLYCRLGLCUXUPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | Cc1c(N)cccc1N |
| Stability | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong acids. |
| Water Solubility | 60 g/L (15 ºC) |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |



GHS07, GHS08, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302 + H312-H317-H341-H411 |
| Precautionary Statements | P273-P280 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful;N:Dangerousfortheenvironment; |
| Risk Phrases | R21/22;R40;R43;R50/53 |
| Safety Phrases | S24-S36/37-S61 |
| RIDADR | UN 3077 9/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | XS9750000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
|
Biological monitoring as a valid tool to assess occupational exposure to mixtures of 2,4-:2,6-toluene diisocyanate.
Med. Lav. 103(5) , 361-71, (2012) Despite its advantages over environmental monitoring, biological monitoring of exposure to 2,4-:2,6-toluene diisocyanate (TDI) mixtures is still underused. The present study was designed in order to e... |
|
|
Air exposure assessment of TDI and biological monitoring of TDA in urine in workers in polyurethane foam industry.
Occup. Environ. Med. 69(2) , 93-8, (2012) Toluene diisocyanate (TDI) is used in the manufacturing process of polyurethane (PU) foams and is a potent inducer of occupational asthma. The objective of this study was to evaluate the correlation b... |
|
|
Improvement in the GC-MS method for determining urinary toluene-diamine and its application to the biological monitoring of workers exposed to toluene-diisocyanate.
Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 78(6) , 459-66, (2005) To develop a simple and sensitive GC-MS method for determining toluene-diamine (TDA) in urine and to apply the method for biological monitoring of workers exposed to toluene-diisocyanate (TDI).After a... |
| 2-Methyl-m-phenylenediamine |
| 2-Methyl-1,3-benzenediamine |
| 2,6-toluenediamine |
| MFCD00007800 |
| 2,6-diaminotoluene |
| 2,6-Tolylenediamine |
| EINECS 212-513-9 |
| 1,3-Benzenediamine, 2-methyl- |
| 2-methylbenzene-1,3-diamine |
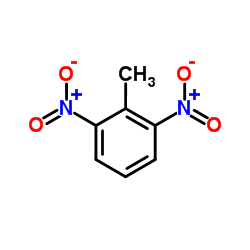 CAS#:606-20-2
CAS#:606-20-2 CAS#:121-14-2
CAS#:121-14-2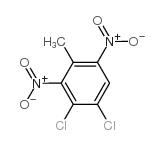 CAS#:53278-85-6
CAS#:53278-85-6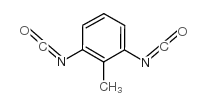 CAS#:91-08-7
CAS#:91-08-7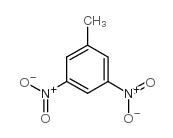 CAS#:618-85-9
CAS#:618-85-9 CAS#:602-01-7
CAS#:602-01-7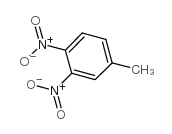 CAS#:610-39-9
CAS#:610-39-9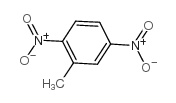 CAS#:619-15-8
CAS#:619-15-8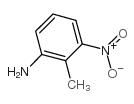 CAS#:603-83-8
CAS#:603-83-8 CAS#:7647-01-0
CAS#:7647-01-0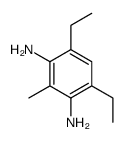 CAS#:2095-01-4
CAS#:2095-01-4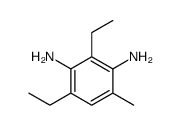 CAS#:2095-02-5
CAS#:2095-02-5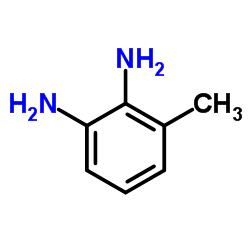 CAS#:2687-25-4
CAS#:2687-25-4 CAS#:584-84-9
CAS#:584-84-9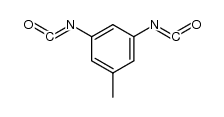 CAS#:14219-05-7
CAS#:14219-05-7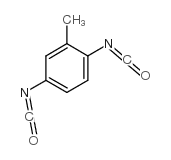 CAS#:614-90-4
CAS#:614-90-4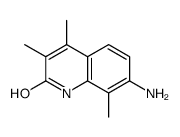 CAS#:125710-04-5
CAS#:125710-04-5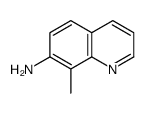 CAS#:116632-62-3
CAS#:116632-62-3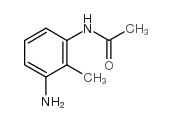 CAS#:65999-76-0
CAS#:65999-76-0
