| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Fructose
CAS:57-48-7 |
|
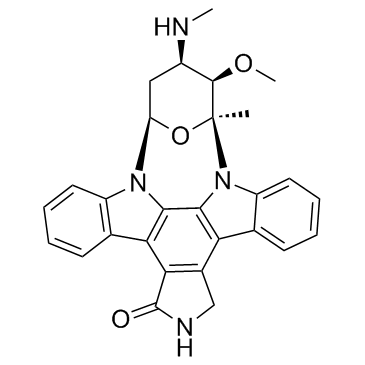 |
Staurosporine
CAS:62996-74-1 |
|
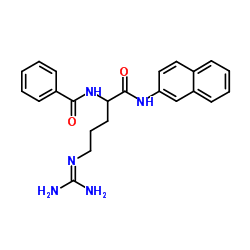 |
bz-dl-arg-betana hcl
CAS:913-04-2 |
|
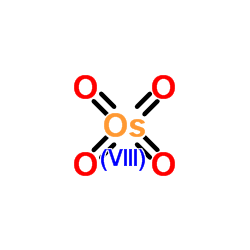 |
Osmium tetroxide
CAS:20816-12-0 |
|
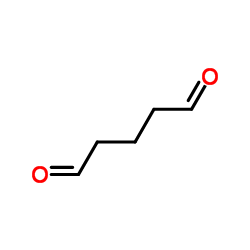 |
glutaraldehyde
CAS:111-30-8 |
|
 |
D-(+)-Trehalose dihydrate
CAS:6138-23-4 |
|
 |
3-Methyladenine
CAS:5142-23-4 |
|
 |
Acarbose
CAS:56180-94-0 |
|
 |
Maltose
CAS:69-79-4 |
|
 |
Thiazolyl Blue
CAS:298-93-1 |