| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
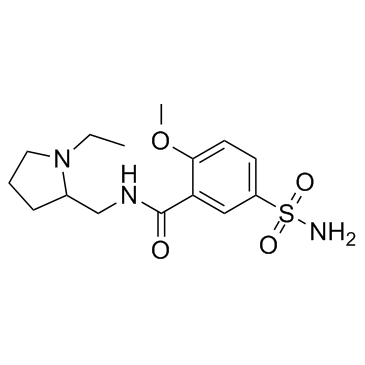 |
Sulpiride
CAS:15676-16-1 |
|
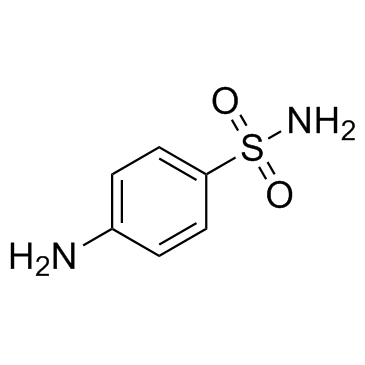 |
Sulfanilamide
CAS:63-74-1 |
|
 |
Saccharin
CAS:81-07-2 |
|
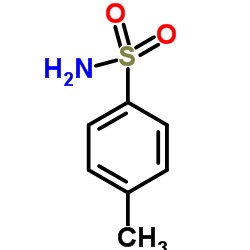 |
4-Toluenesulfonamide
CAS:70-55-3 |
|
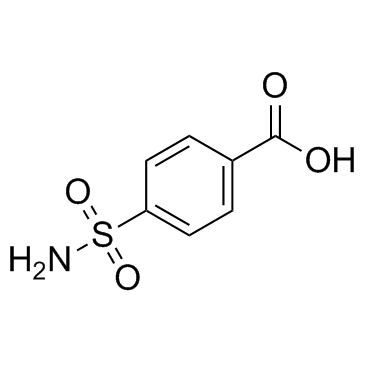 |
Carzenide
CAS:138-41-0 |