| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
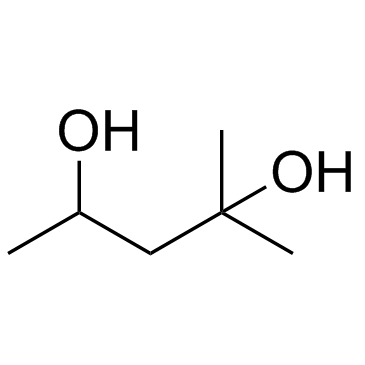 |
Hexylene glycol
CAS:107-41-5 |
|
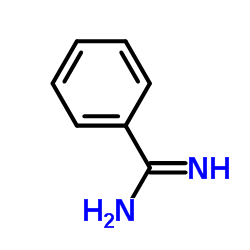 |
Benzamidine
CAS:618-39-3 |
|
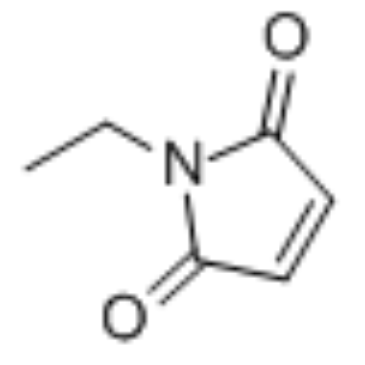 |
N-ethylmaleimide
CAS:128-53-0 |
|
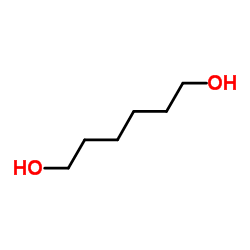 |
Hexan-1,6-diol
CAS:629-11-8 |
|
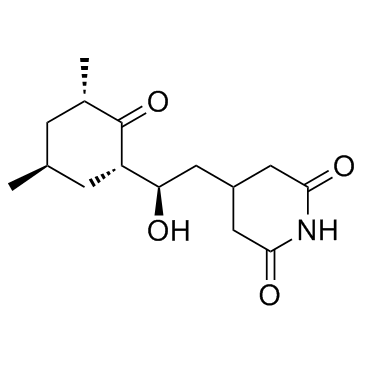 |
Cycloheximide
CAS:66-81-9 |
|
 |
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
CAS:60-00-4 |
|
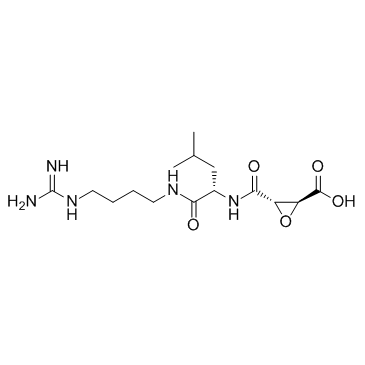 |
E-64
CAS:66701-25-5 |