| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Erythromycin
CAS:114-07-8 |
|
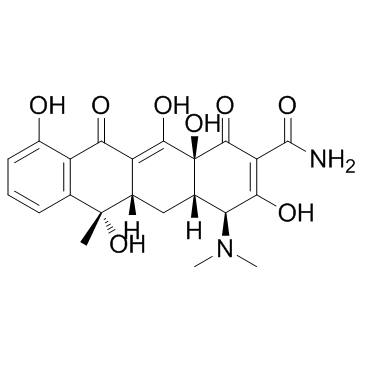 |
Tetracycline
CAS:60-54-8 |
|
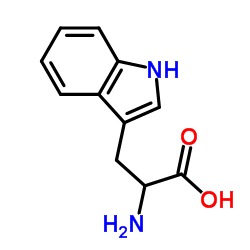 |
DL-Tryptophan
CAS:54-12-6 |
|
 |
Xanthurenic acid
CAS:59-00-7 |
|
 |
Kynurenic acid
CAS:492-27-3 |
|
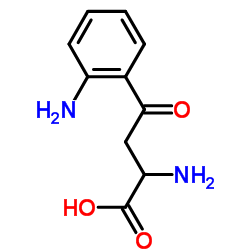 |
Kynurenine
CAS:343-65-7 |
|
 |
L(-)-Tryptophan
CAS:73-22-3 |
|
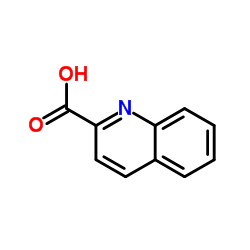 |
Quinoline-2-carboxylic acid
CAS:93-10-7 |
|
 |
3-hydroxy-dl-kynurenine
CAS:2147-61-7 |