| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
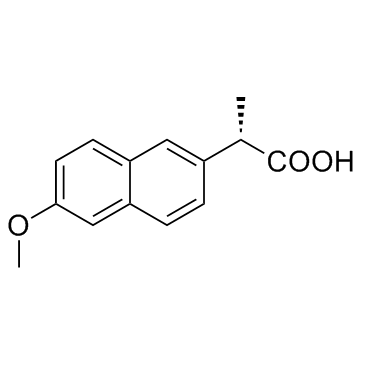 |
Naproxen
CAS:22204-53-1 |
|
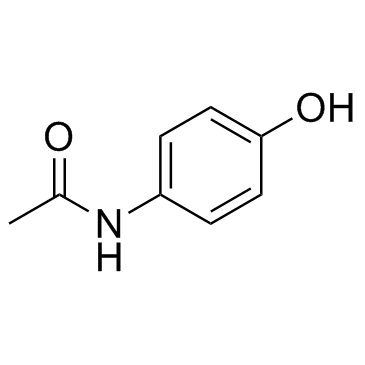 |
4-Acetamidophenol
CAS:103-90-2 |
|
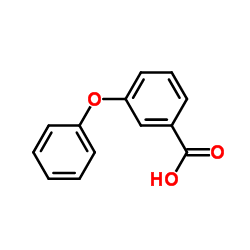 |
3-Phenoxybenzoic acid
CAS:3739-38-6 |
|
 |
Aspirin
CAS:50-78-2 |
|
 |
2-Benzoylbenzoic acid
CAS:85-52-9 |
|
 |
4-methybenzophenone
CAS:134-84-9 |
|
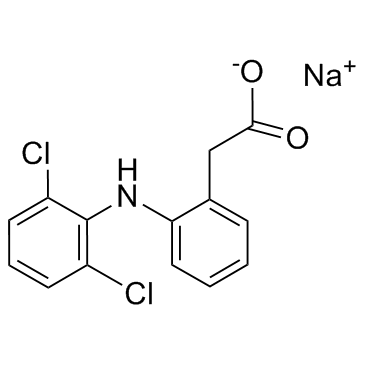 |
Diclofenac sodium
CAS:15307-79-6 |
|
 |
ketoprofen
CAS:22071-15-4 |
|
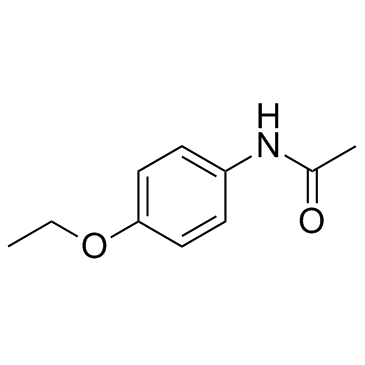 |
Phenacetin
CAS:62-44-2 |
|
 |
Ibuprofen
CAS:15687-27-1 |