| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
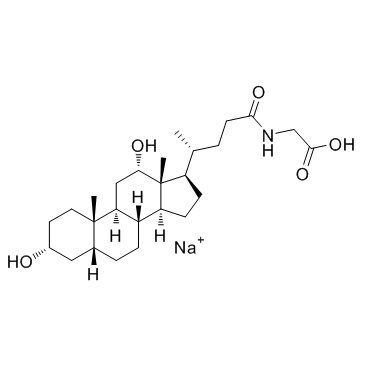 |
Glycodeoxycholate Sodium
CAS:16409-34-0 |
|
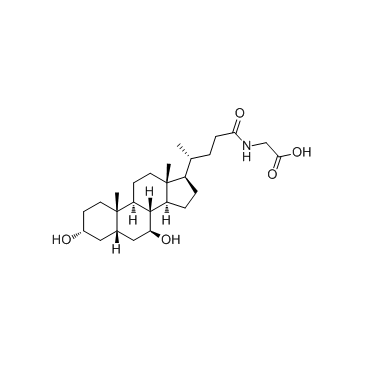 |
Glycoursodeoxycholic acid
CAS:64480-66-6 |
|
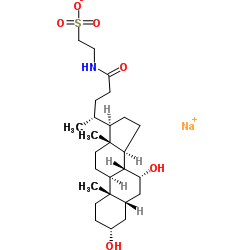 |
Taurochenodeoxycholic acid sodium salt
CAS:6009-98-9 |
|
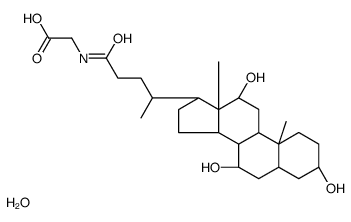 |
Glycocholic acid (hydrate)
CAS:1192657-83-2 |