| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
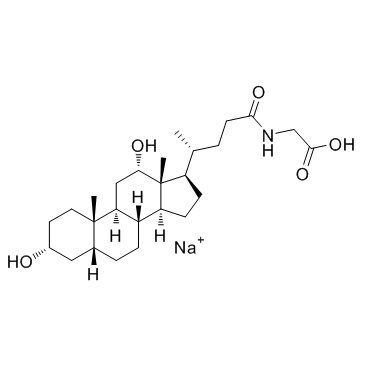 |
甘氨脱氧胆酸钠
CAS:16409-34-0 |
|
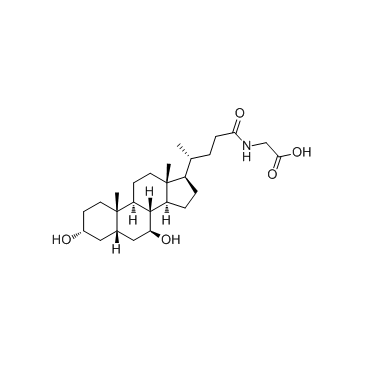 |
甘氨熊去氧胆酸
CAS:64480-66-6 |
|
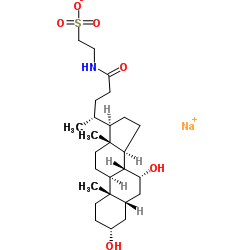 |
牛磺鹅去氧胆酸钠
CAS:6009-98-9 |
|
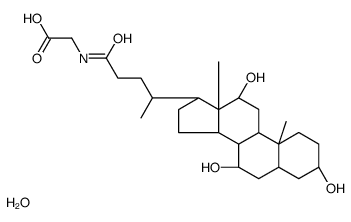 |
甘胆酸
CAS:1192657-83-2 |