| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
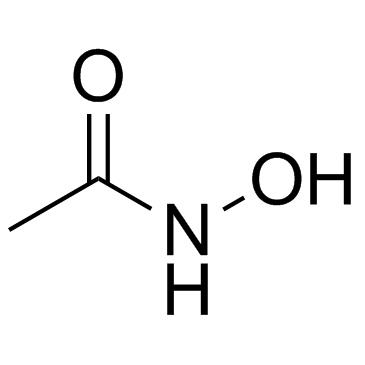 |
Acetohydroxamic acid
CAS:546-88-3 |
|
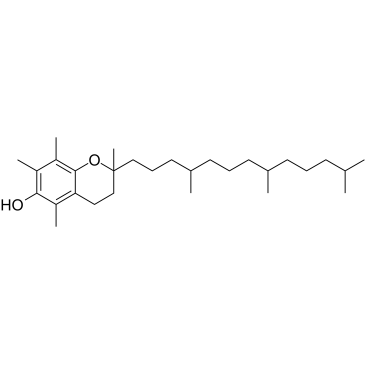 |
Vitamin E
CAS:10191-41-0 |
|
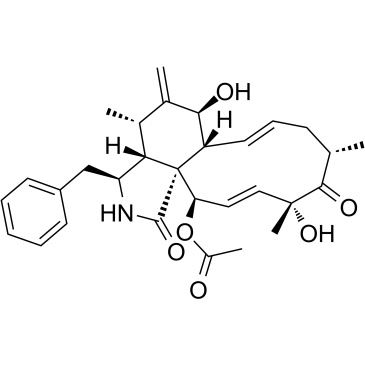 |
Lygosporin A
CAS:22144-77-0 |
|
 |
Colchicine
CAS:64-86-8 |
|
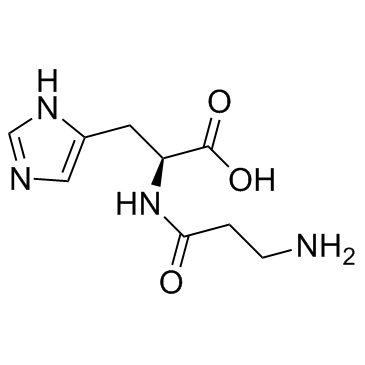 |
L-carnosine
CAS:305-84-0 |
|
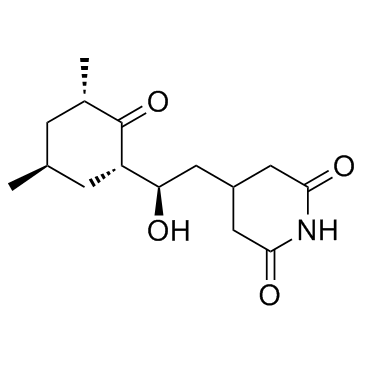 |
Cycloheximide
CAS:66-81-9 |
|
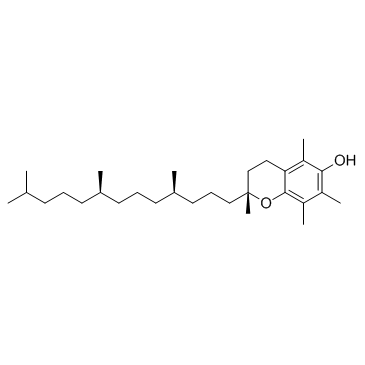 |
DL-alpha-Tocopherol
CAS:59-02-9 |
|
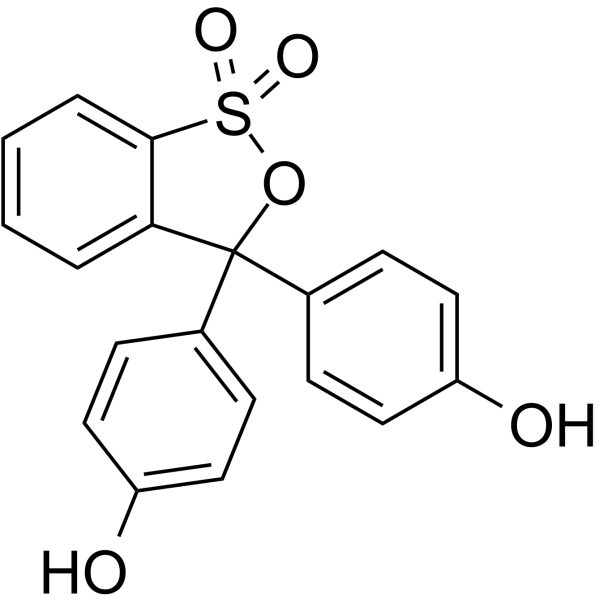 |
Phenol red
CAS:143-74-8 |
|
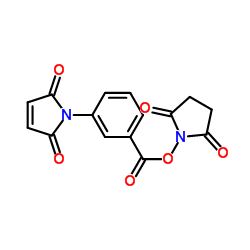 |
MBS Crosslinker
CAS:58626-38-3 |
|
 |
Nocodazole
CAS:31430-18-9 |