Nocodazole
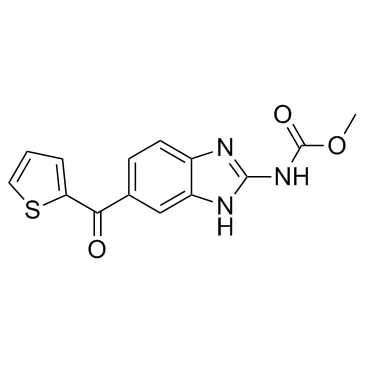
Nocodazole structure
|
Common Name | Nocodazole | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 31430-18-9 | Molecular Weight | 301.320 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H11N3O3S | Melting Point | 300 °C (dec.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS08 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of NocodazoleNocodazole is a rapidly-reversible inhibitor of microtubule. Nocodazole binds to β-tubulin and disrupts microtubule assembly/disassembly dynamics, which prevents mitosis and induces apoptosis in tumor cells. |
| Name | nocodazole |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Nocodazole is a rapidly-reversible inhibitor of microtubule. Nocodazole binds to β-tubulin and disrupts microtubule assembly/disassembly dynamics, which prevents mitosis and induces apoptosis in tumor cells. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Abl:91 nM (Kd) ABL(E255K):120 nM (Kd) ABL(T315I):170 nM (Kd) BRAF:1.8 μM (Kd) BRAF(V600E):1.1 μM (Kd) c-KIT:1.6 μM (Kd) MEK1:1.7 μM (Kd) MEK2:1.6 μM (Kd) MET:1.7 μM (Kd) PI3Kγ:1.5 μM (Kd) Microtubule/Tubulin CRISPR/Cas9 |
| In Vitro | Nocodazole exhibits good affinity toward c-KIT, with a Kd value of 1.6 μM in highly malignant human cancer cells. Nocodazole displays good binding affinity toward the components of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway, such as BRAF (Kd=1.8 μM), BRAF(V600E) (Kd=1.1 μM), MEK1 (Kd=1.7 μM), and MEK2 (Kd=1.6 μM)[1]. Nocodazole has the highest affinity for αβIV and the lowest affinity for αβIII[2]. After release from the nocodazole block, cells synchronized in mitosis remaine sensitive to very low concentrations of paclitaxel for < 30 min, the time required for spindle formation, yet remains sensitive to vinblastine for > 90 min[3]. Nocodazole (1 nM) induces apoptosis of COLO 205 cancer cells[4]. Nocodazole (≥ 30 µg/mL) significantly increases the percentage of annexin-V-binding cells without significantly modifying average forward scatter of human erythrocytes[5]. |
| In Vivo | Nocodazole (5 mg/kg/three times per week, i.p.) has antitumor effects in athymic mice bearing COLO 205 tumor xenografts. Nocodazole (1 nM) + ketoconazole dramatically increase the levels of p21/CIP1 and p27/KIP1 protein in the tumor tissues[4]. |
| Cell Assay | Proteins are loaded at 50 μg/lane and separated by 12% (w:v) sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, blotted, and probed with antibodies for cyclin E, p53, p21/CIP1, p27/KIP1, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), cyclin A, cyclin D1, cyclin D3, cyclin B, CDK2, CDK4, and cytochrome C. Immunoreactive bands are visualized by incubating with the colorigenic substrates nitroblue tetrazolium and 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-phosphate. The expression of GAPDH is used as the control for equal protein loading. |
| Animal Admin | COLO 205 cells are grown in RPMI 1640 supplemented with 10% FCS. Cells are harvested through two consecutive trypsinizations, centrifuged at 300×g; for 5 min, washed twice, and resuspended in sterile phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). Cells (5×105) in 0.1 mL are injected subcutaneously between the scapulae of each nude mouse. After transplantation, tumor size is measured with calipers, and the tumor volume is estimated. Once tumors reach a mean size of 200 mm3, animals receive intraperitoneal injections of DMSO (25 μL), ketoconazole (50 mg/kg), nocodazole (5 mg/kg), or ketoconazole + nocodazole three times per week for 6 wk. |
| References |
[2]. Keliang Xu, et al. Interaction of nocodazole with tubulin isotypes. Drug Development Research 2002 |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 300 °C (dec.) |
| Molecular Formula | C14H11N3O3S |
| Molecular Weight | 301.320 |
| Exact Mass | 301.052124 |
| PSA | 112.32000 |
| LogP | 2.43 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.732 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Water Solubility | DMSO: 10 mg/mL, soluble |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H341-H361d |
| Precautionary Statements | P281 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | T: Toxic; |
| Risk Phrases | R61 |
| Safety Phrases | S53-S45-S36/37/39-S26 |
| RIDADR | 2811 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | DD6521000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(b) |
| HS Code | 2934999090 |
|
~21% 
Nocodazole CAS#:31430-18-9 |
| Literature: European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 24, p. 363 - 370 |
| HS Code | 2934999090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2934999090. other heterocyclic compounds. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
SHCBP1 is required for midbody organization and cytokinesis completion.
Cell Cycle 13(17) , 2744-51, (2014) The centralspindlin complex, which is composed of MKLP1 and MgcRacGAP, is one of the crucial factors involved in cytokinesis initiation. Centralspindlin is localized at the middle of the central spind... |
|
|
MeCP2 deficiency is associated with reduced levels of tubulin acetylation and can be restored using HDAC6 inhibitors.
J. Mol. Med. 93(1) , 63-72, (2015) Rett syndrome (RTT) is a severe neurodevelopmental disorder, predominantly caused by loss of function mutations in the X-linked methyl-CpG-binding protein 2 (MECP2) gene. Despite the genetic cause bei... |
|
|
EphA receptors regulate prostate cancer cell dissemination through Vav2-RhoA mediated cell-cell repulsion.
Biol. Open 3(6) , 453-62, (2014) Metastatic prostate cancer cells display EphB receptor-mediated attraction when they contact stromal fibroblasts but EphA-driven repulsion when they contact one another. The impact of these 'social' i... |
| 2-Benzimidazolecarbamic acid, 5-(2-thienylcarbonyl)-, methyl ester |
| Methyl N-(5-thenoyl-2-benzimidazolyl)carbamate |
| methyl N-[6-(thiophene-2-carbonyl)-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl]carbamate |
| Methyl [5-(2-thienylcarbonyl)-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl]carbamate |
| Nocodazole |
| Nocidazole |
| 2-Benzimidazolecarbamic acid, 5-(2-thienoyl)-, methyl ester |
| Methyl 5-(2-thienoyl)-2-benzimidazolecarbamate |
| nocodazolum |
| Nocodazol |
| methyl [5-(thiophen-2-ylcarbonyl)-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl]carbamate |
| EINECS 250-626-5 |
| Carbamic acid, N-[5-(2-thienylcarbonyl)-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl]-, methyl ester |
| Oncodazole |
| MFCD00005588 |
| methyl 5-(thiophene-2-carbonyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-ylcarbamate |
![(S)-2-((S)-2-aminopropanamido)-2-(2-((methoxycarbonyl)amino)-5-(thiophene-2-carbonyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)acetic acid structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/179/127590-63-0.png)

