| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
N-hexane
CAS:110-54-3 |
|
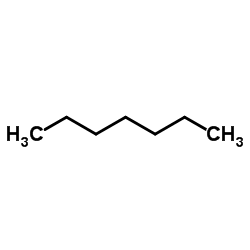 |
Heptane
CAS:142-82-5 |
|
 |
Acetonitrile
CAS:75-05-8 |
|
 |
Formic Acid
CAS:64-18-6 |
|
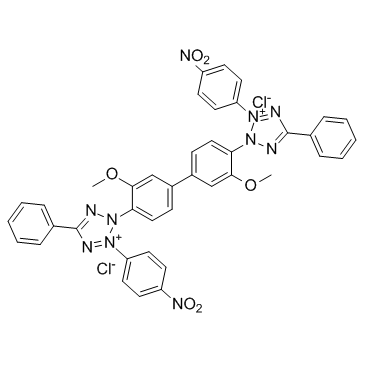 |
NBT
CAS:298-83-9 |
|
 |
triacontane
CAS:638-68-6 |
|
 |
Retinoic acid
CAS:302-79-4 |
|
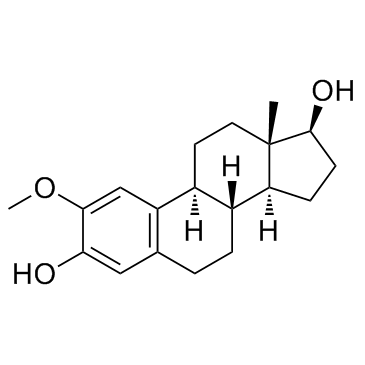 |
2-Methoxyestradiol
CAS:362-07-2 |
|
 |
Tetrazolium blue
CAS:1871-22-3 |
|
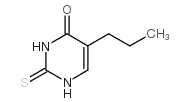 |
5-propyl-2-thiouracil
CAS:2954-52-1 |