| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Acetone
CAS:67-64-1 |
|
 |
Acetonitrile
CAS:75-05-8 |
|
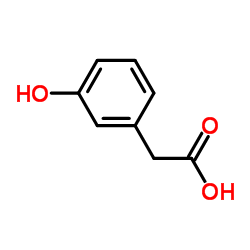 |
3-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid
CAS:621-37-4 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
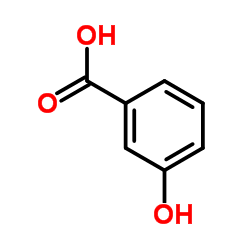 |
3-Hydroxybenzoicacid
CAS:99-06-9 |
|
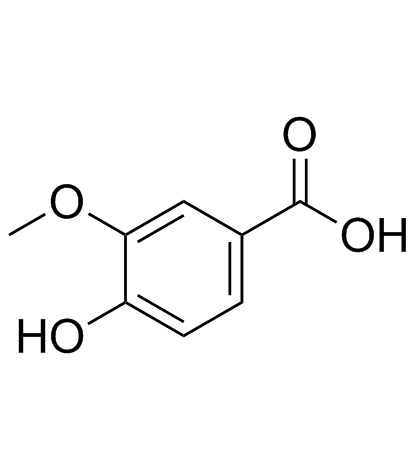 |
Vanillic acid
CAS:121-34-6 |
|
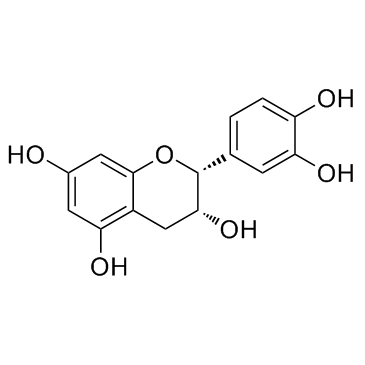 |
Epicatechin
CAS:490-46-0 |
|
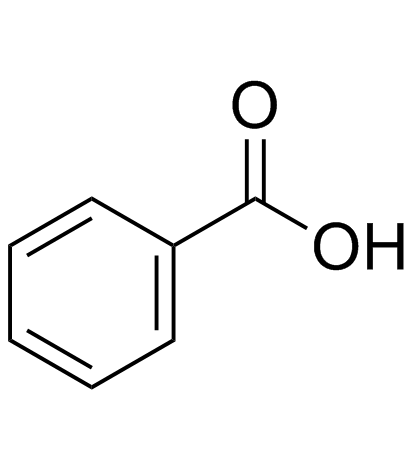 |
benzoic acid
CAS:65-85-0 |
|
 |
acetic acid
CAS:64-19-7 |
|
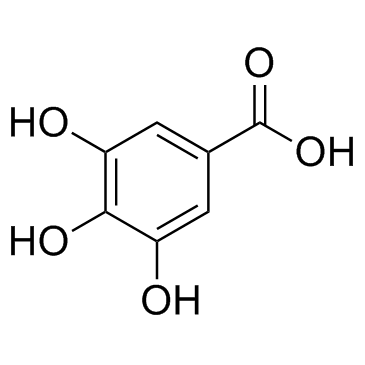 |
Gallic acid
CAS:149-91-7 |