| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Acetone
CAS:67-64-1 |
|
 |
Acetonitrile
CAS:75-05-8 |
|
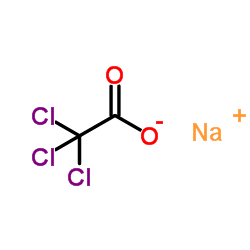 |
Sodium TCA
CAS:650-51-1 |
|
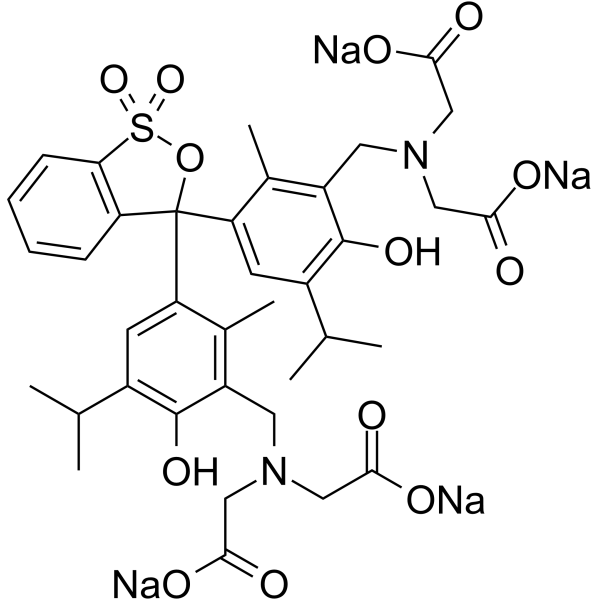 |
methylthymol blue
CAS:1945-77-3 |
|
 |
D-(+)-Glucose
CAS:50-99-7 |
|
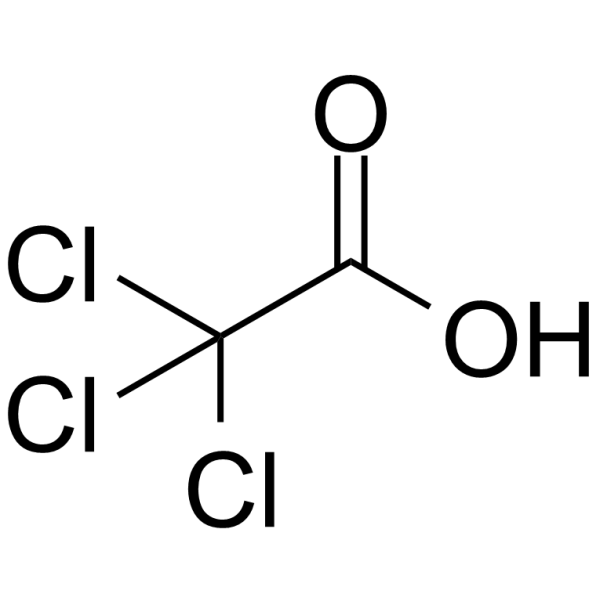 |
Trichloroacetic acid
CAS:76-03-9 |
|
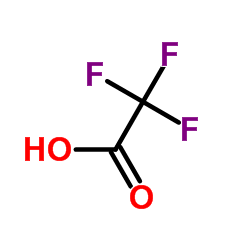 |
trifluoroacetic acid
CAS:76-05-1 |