| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Acetone
CAS:67-64-1 |
|
 |
Hydrochloric acid
CAS:7647-01-0 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
 |
Dichloromethane
CAS:75-09-2 |
|
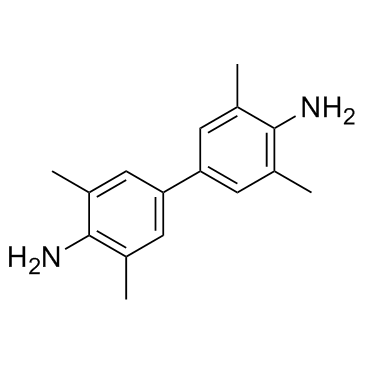 |
Tetramethylbenzidine
CAS:54827-17-7 |
|
 |
Dimethyl sulfoxide
CAS:67-68-5 |
|
 |
Calcium chloride
CAS:10043-52-4 |
|
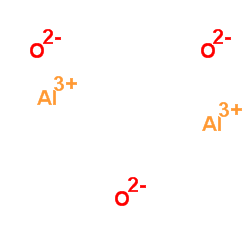 |
Aluminum oxide
CAS:1344-28-1 |
|
 |
Suc-Ala-Ala-Pro-Phe-pNA
CAS:70967-97-4 |
|
 |
ethyl acetate
CAS:141-78-6 |