| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Ethanol
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
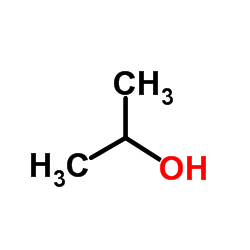 |
Isopropanol
CAS:67-63-0 |
|
 |
Iodoacetic acid
CAS:64-69-7 |
|
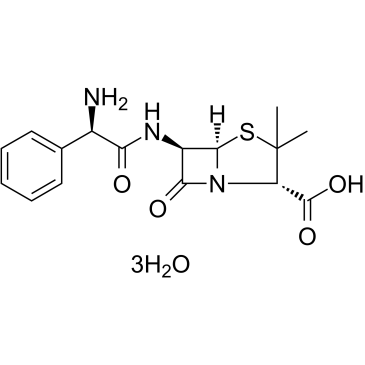 |
Ampicillin Trihydrate
CAS:7177-48-2 |
|
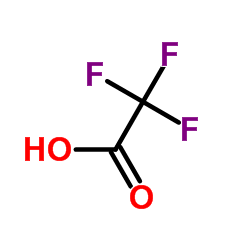 |
trifluoroacetic acid
CAS:76-05-1 |
|
 |
Ampicillin
CAS:69-53-4 |
|
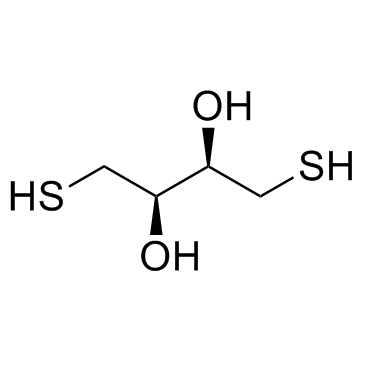 |
DL-Dithiothreitol
CAS:3483-12-3 |
|
 |
amberlite(r) xad-1180
CAS:9003-69-4 |