| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Ethanol
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
 |
Astemizole
CAS:68844-77-9 |
|
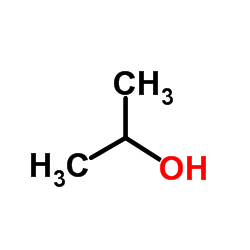 |
Isopropanol
CAS:67-63-0 |
|
 |
Dimethyl sulfoxide
CAS:67-68-5 |
|
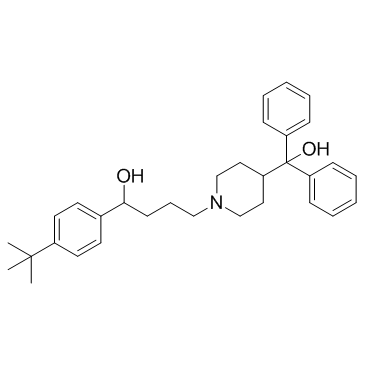 |
Terfenadine
CAS:50679-08-8 |
|
 |
Loratadine
CAS:79794-75-5 |