| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
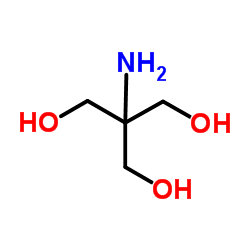 |
Trometamol
CAS:77-86-1 |
|
 |
Glycine
CAS:56-40-6 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
 |
sodium dodecyl sulfate
CAS:151-21-3 |
|
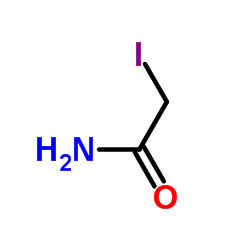 |
Iodoacetamide
CAS:144-48-9 |
|
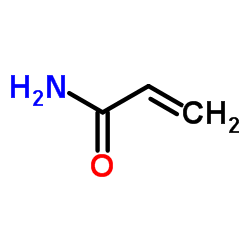 |
Acrylamide Crystals
CAS:79-06-1 |
|
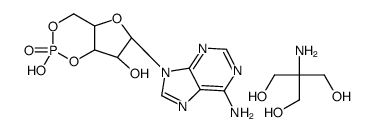 |
ADENOSINE 3':5'-CYCLIC MONOPHOSPHATE TRIS SALT
CAS:102029-77-6 |
|
 |
DL-Serine
CAS:302-84-1 |
|
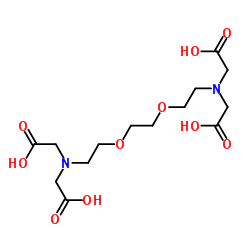 |
EGTA
CAS:67-42-5 |
|
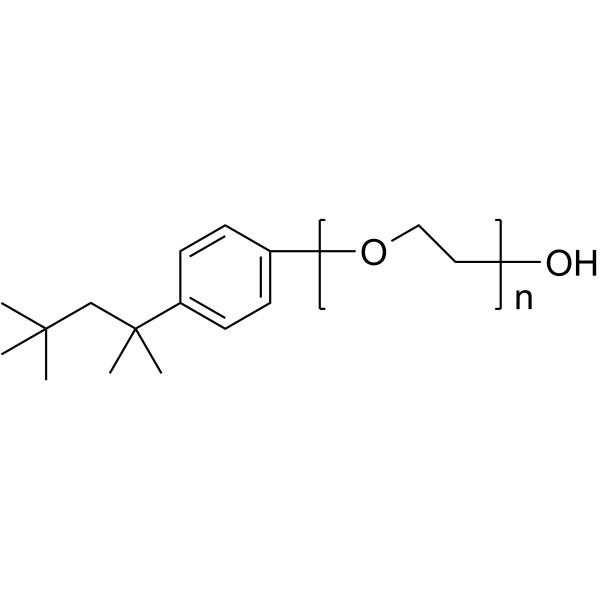 |
Triton X-100
CAS:9002-93-1 |