| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
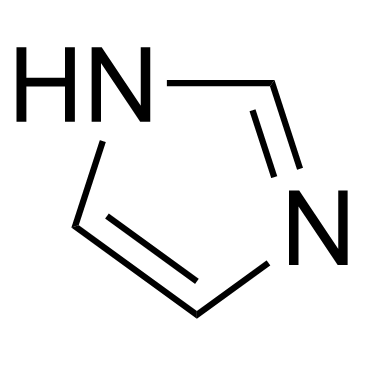 |
Imidazole
CAS:288-32-4 |
|
 |
Hydrochloric acid
CAS:7647-01-0 |
|
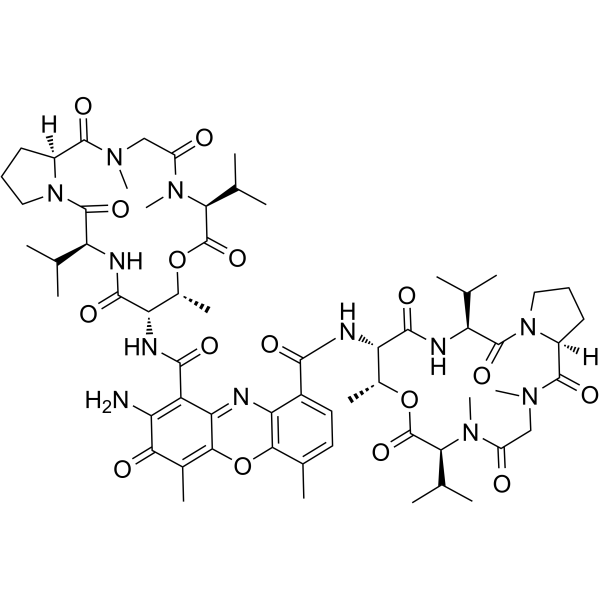 |
Actinomycin D
CAS:50-76-0 |
|
 |
SODIUM CHLORIDE-35 CL
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
 |
Glycerol
CAS:56-81-5 |
|
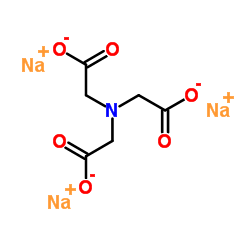 |
SODIUM NITRILOTRIACETATE
CAS:5064-31-3 |
|
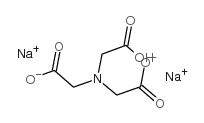 |
Disodium nitrilotriacetate
CAS:15467-20-6 |
|
 |
Magnesium choride
CAS:7786-30-3 |
|
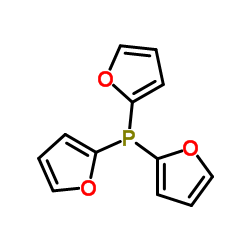 |
Tri(2-furyl)phosphine
CAS:5518-52-5 |