| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
 |
Water
CAS:7732-18-5 |
|
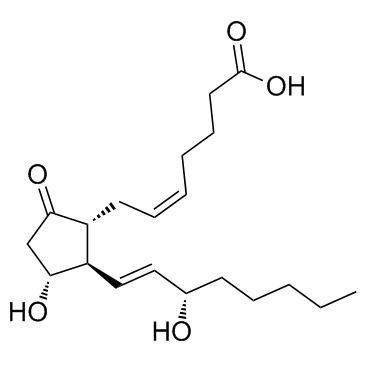 |
Dinoprostone
CAS:363-24-6 |
|
 |
SODIUM CHLORIDE-35 CL
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
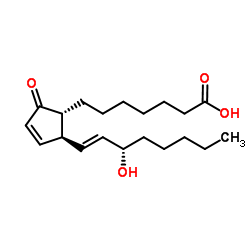 |
PROSTAGLANDIN A1
CAS:14152-28-4 |
|
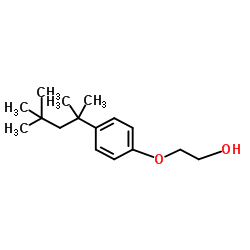 |
2-(4-(1,1,3,3-Tetramethylbutyl)phenoxy)ethanol
CAS:2315-67-5 |
|
 |
4',6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride
CAS:28718-90-3 |
|
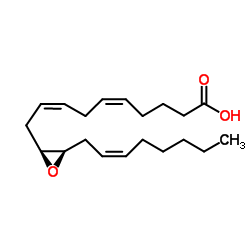 |
(11S,12R)-EET
CAS:123931-40-8 |
|
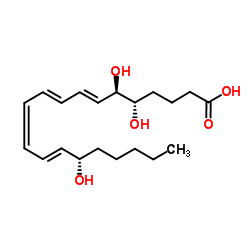 |
Lipoxin A4
CAS:89663-86-5 |