| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
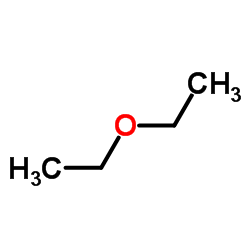 |
Diethyl ether
CAS:60-29-7 |
|
 |
Formic Acid
CAS:64-18-6 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
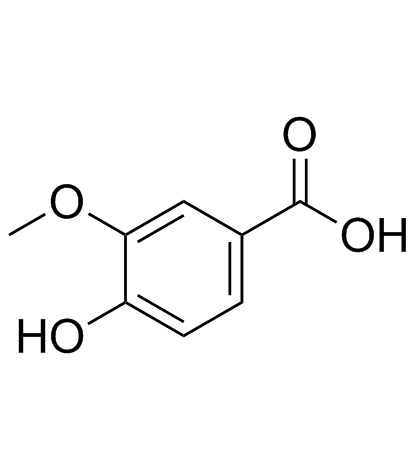 |
Vanillic acid
CAS:121-34-6 |
|
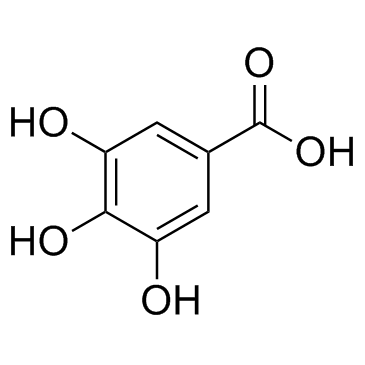 |
Gallic acid
CAS:149-91-7 |
|
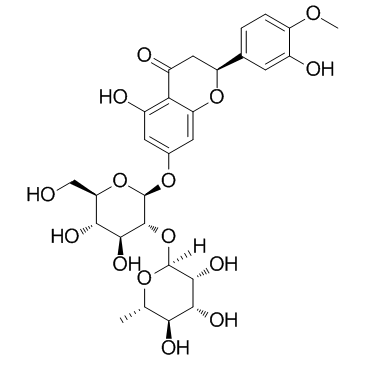 |
Neohesperidin
CAS:13241-33-3 |
|
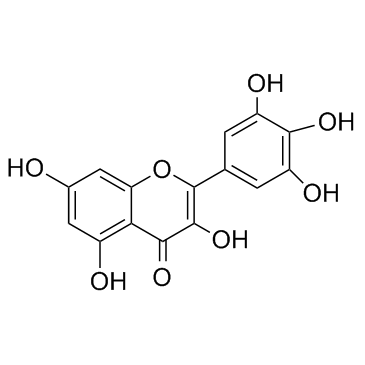 |
Myricetin
CAS:529-44-2 |
|
 |
trans-4-Hydroxycinnamic acid
CAS:501-98-4 |
|
 |
Syringic acid
CAS:530-57-4 |