| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sodium hydroxide
CAS:1310-73-2 |
|
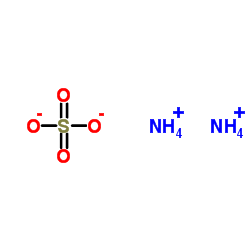 |
ammonium sulphate
CAS:7783-20-2 |
|
 |
3-Ethyl-2,4-pentanedione
CAS:1540-34-7 |
|
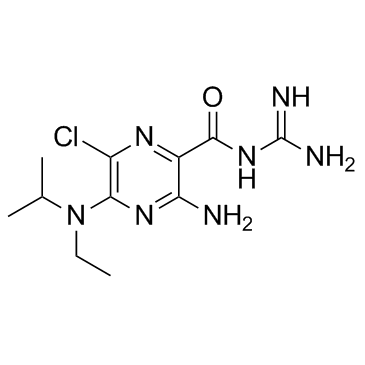 |
EIPA
CAS:1154-25-2 |
|
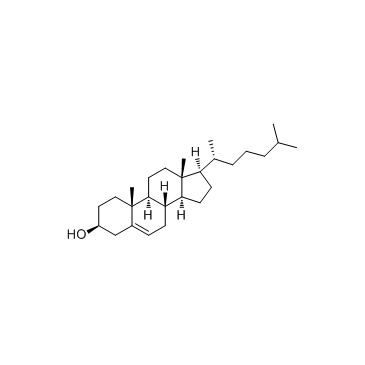 |
cholesterol
CAS:57-88-5 |
|
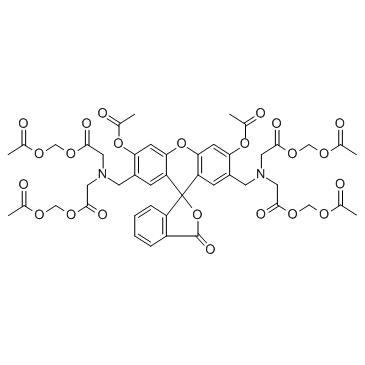 |
Calcein-AM
CAS:148504-34-1 |
|
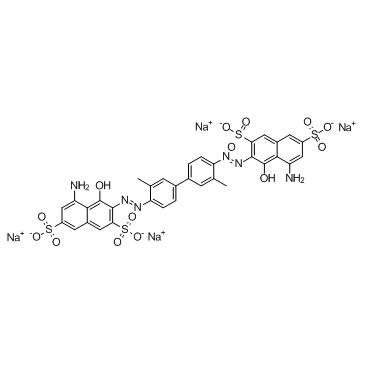 |
Direct Blue 14
CAS:72-57-1 |
|
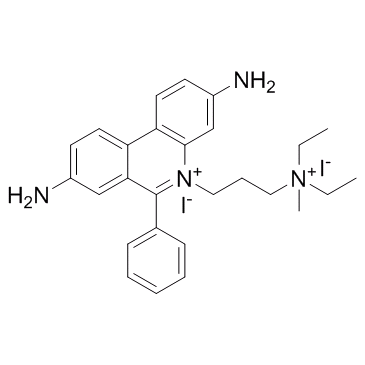 |
Propidium Iodide
CAS:25535-16-4 |
|
 |
Hoechst 33342
CAS:23491-52-3 |