| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sodium hydroxide
CAS:1310-73-2 |
|
 |
Water
CAS:7732-18-5 |
|
 |
Arachidonic acid
CAS:506-32-1 |
|
 |
3-Ethyl-2,4-pentanedione
CAS:1540-34-7 |
|
 |
ADENOSINE 3':5'-CYCLIC MONOPHOSPHATE TRIS SALT
CAS:102029-77-6 |
|
 |
Guanosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate
CAS:7665-99-8 |
|
 |
ODQ
CAS:41443-28-1 |
|
 |
guanosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate sodium salt
CAS:40732-48-7 |
|
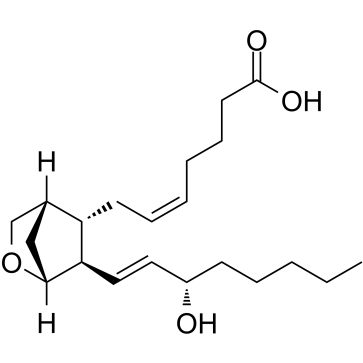 |
U-46619
CAS:56985-40-1 |
|
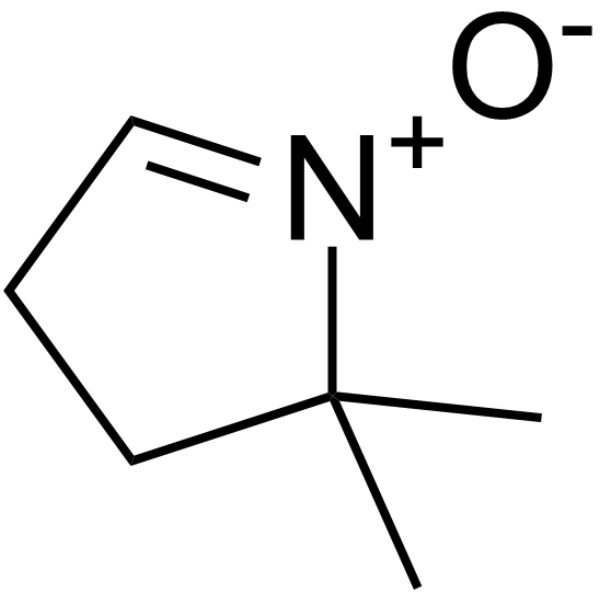 |
DMPO
CAS:3317-61-1 |