| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
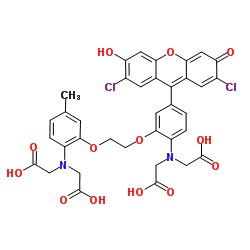 |
Fluo-3
CAS:123632-39-3 |
|
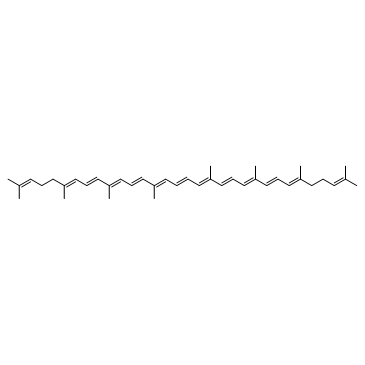 |
Lycopene
CAS:502-65-8 |
|
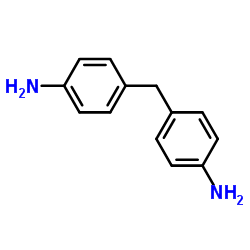 |
4,4′-methylenedianiline
CAS:101-77-9 |
|
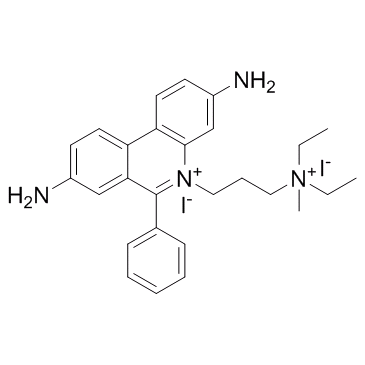 |
Propidium Iodide
CAS:25535-16-4 |
|
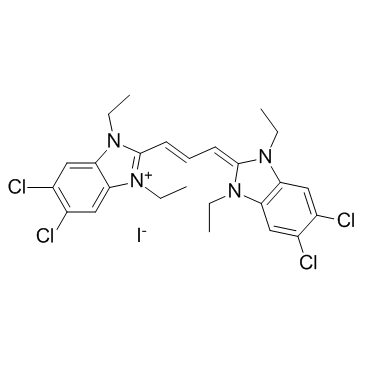 |
JC-1
CAS:3520-43-2 |