| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sodium Fluoride
CAS:7681-49-4 |
|
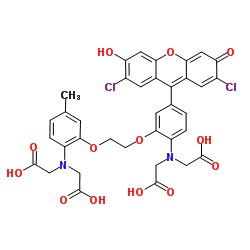 |
Fluo-3
CAS:123632-39-3 |
|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
sodium dodecyl sulfate
CAS:151-21-3 |
|
 |
Acetylcysteine(N-acetylcysteine)
CAS:616-91-1 |
|
 |
Dihydrorhodamine 123
CAS:109244-58-8 |
|
 |
SODIUM CHLORIDE-35 CL
CAS:20510-55-8 |